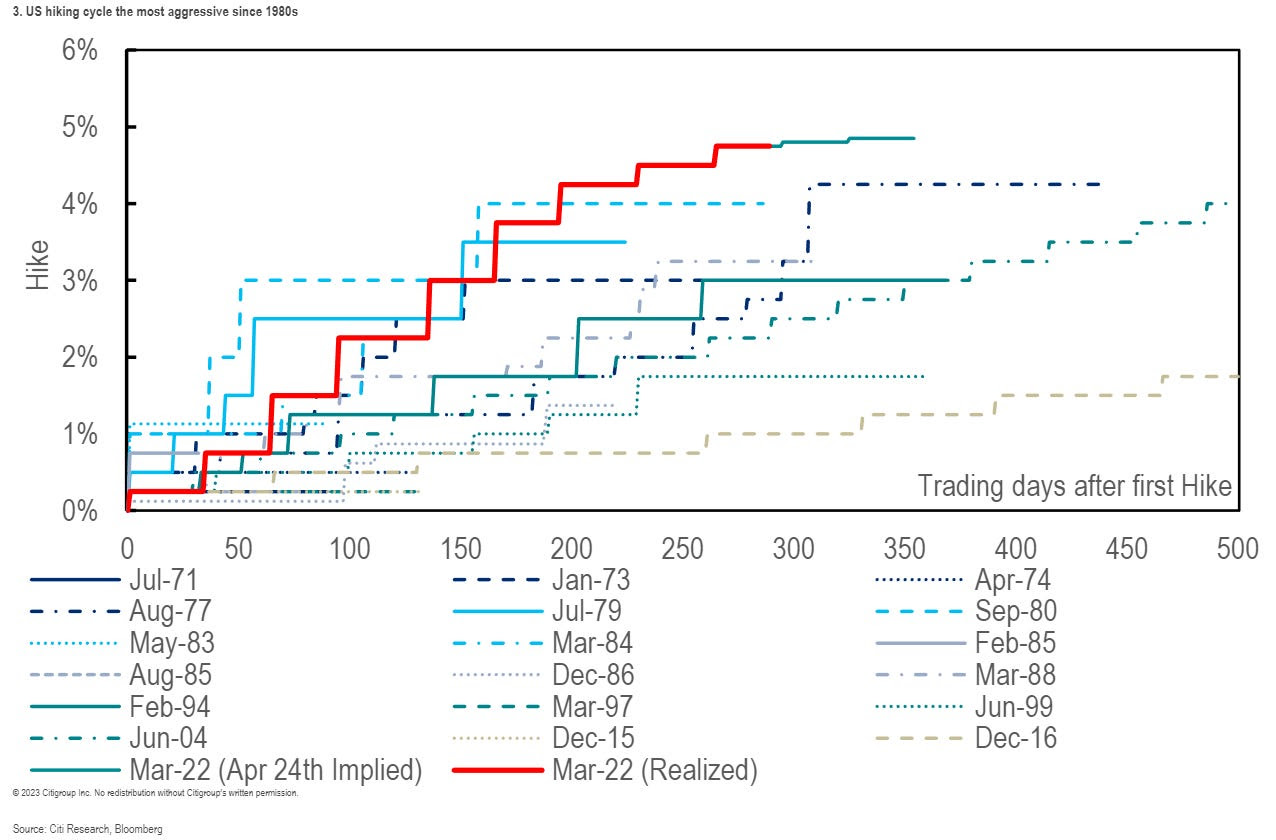
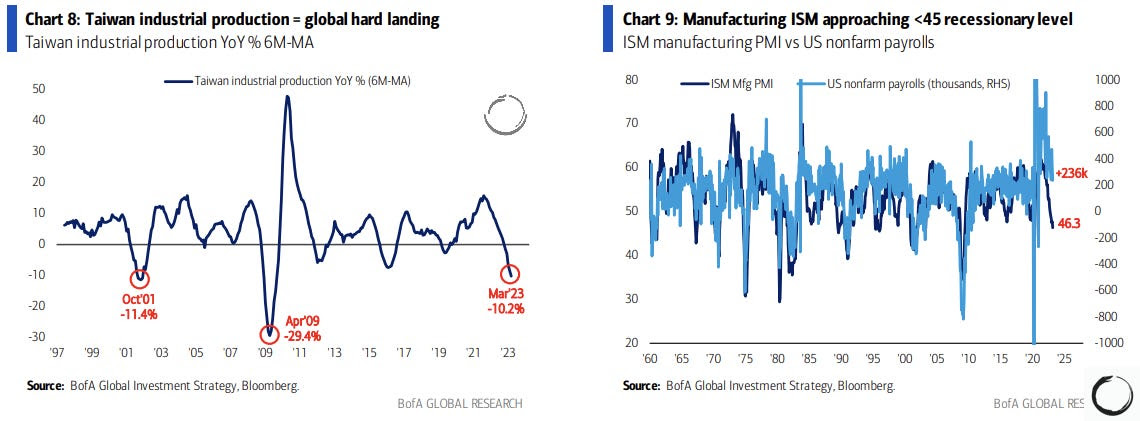
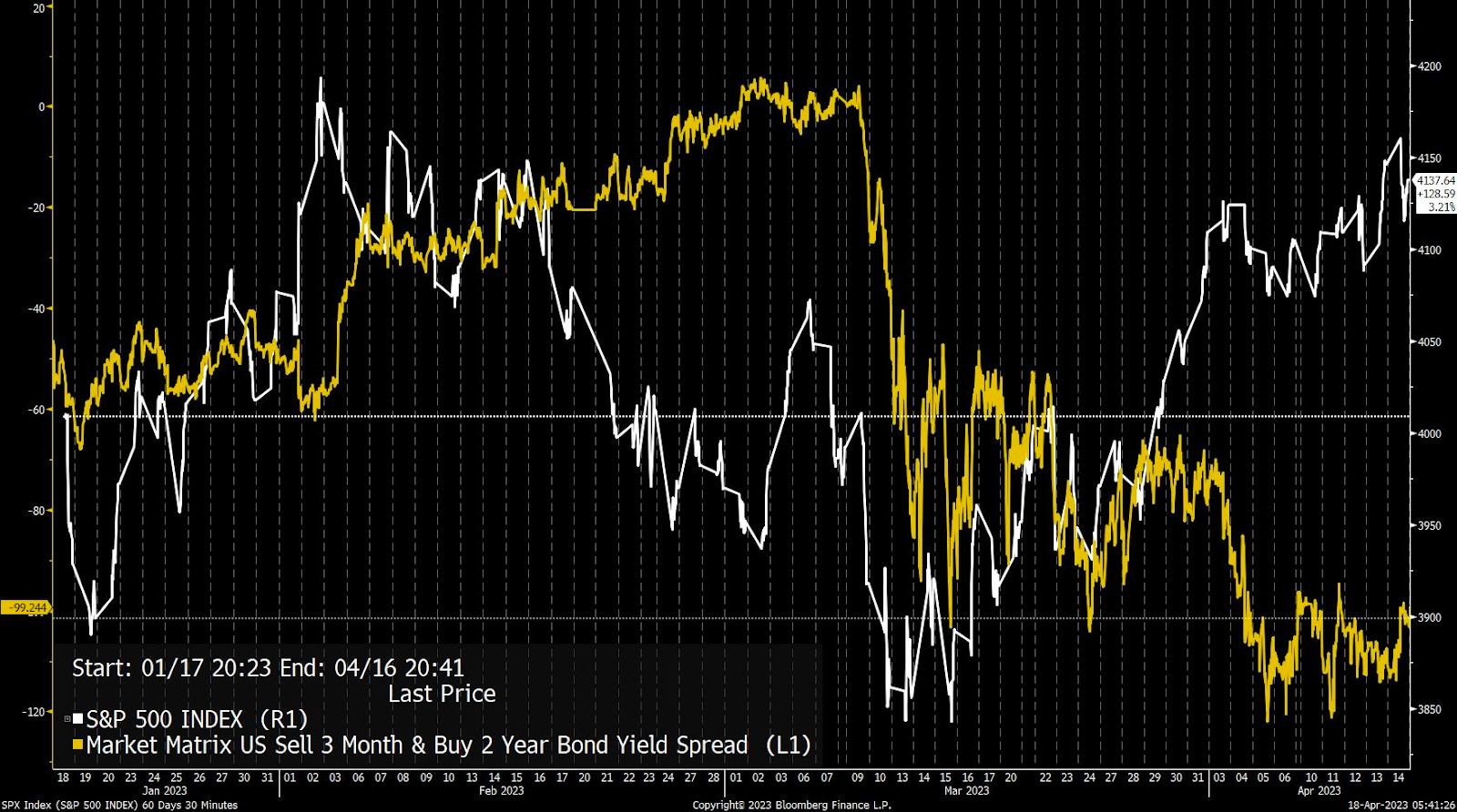
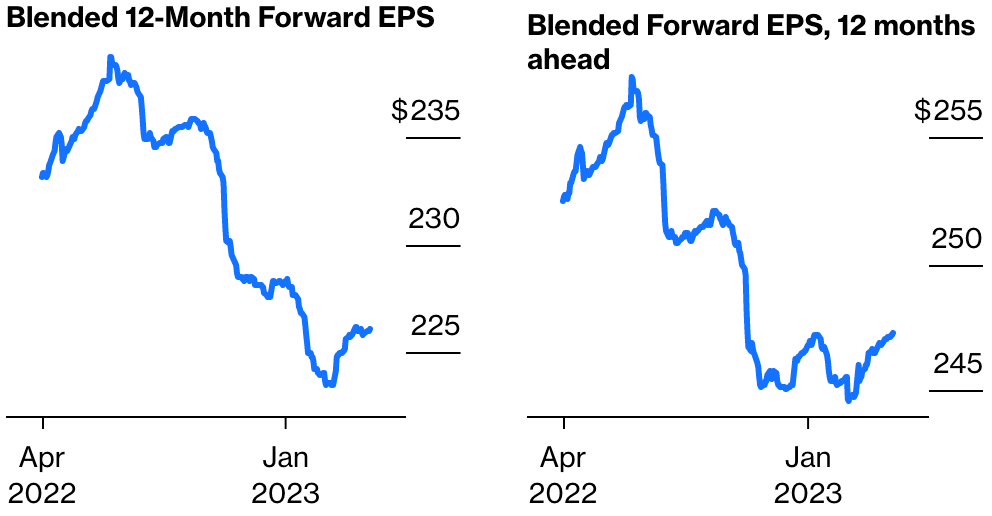
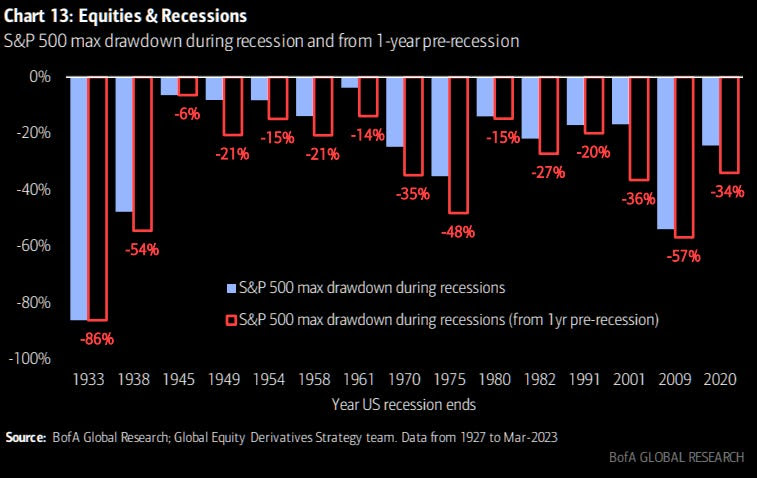
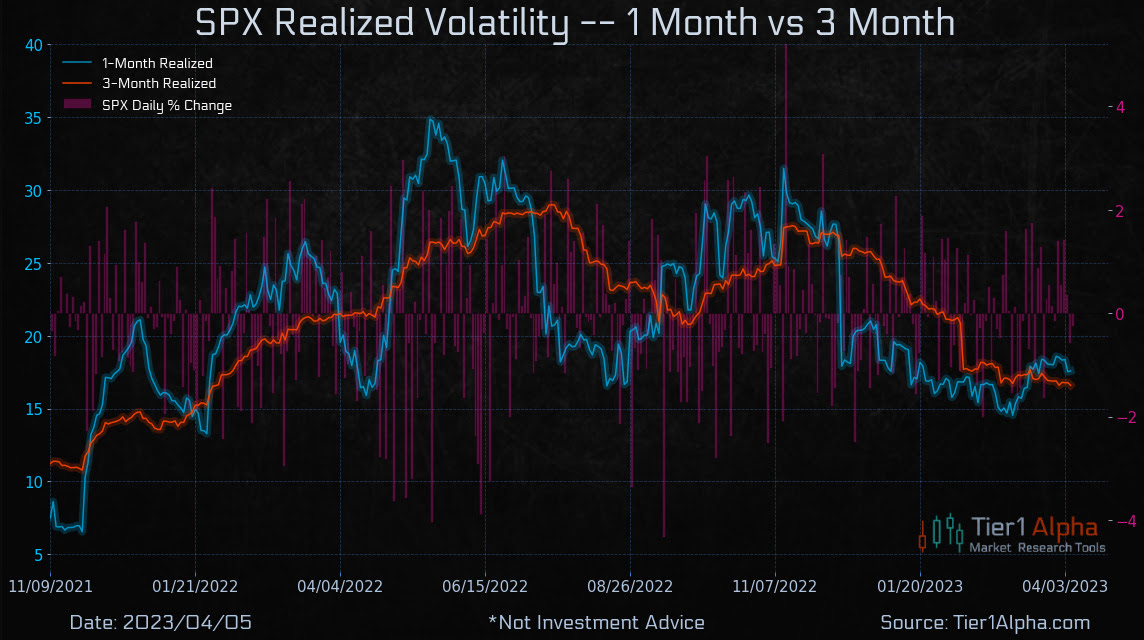
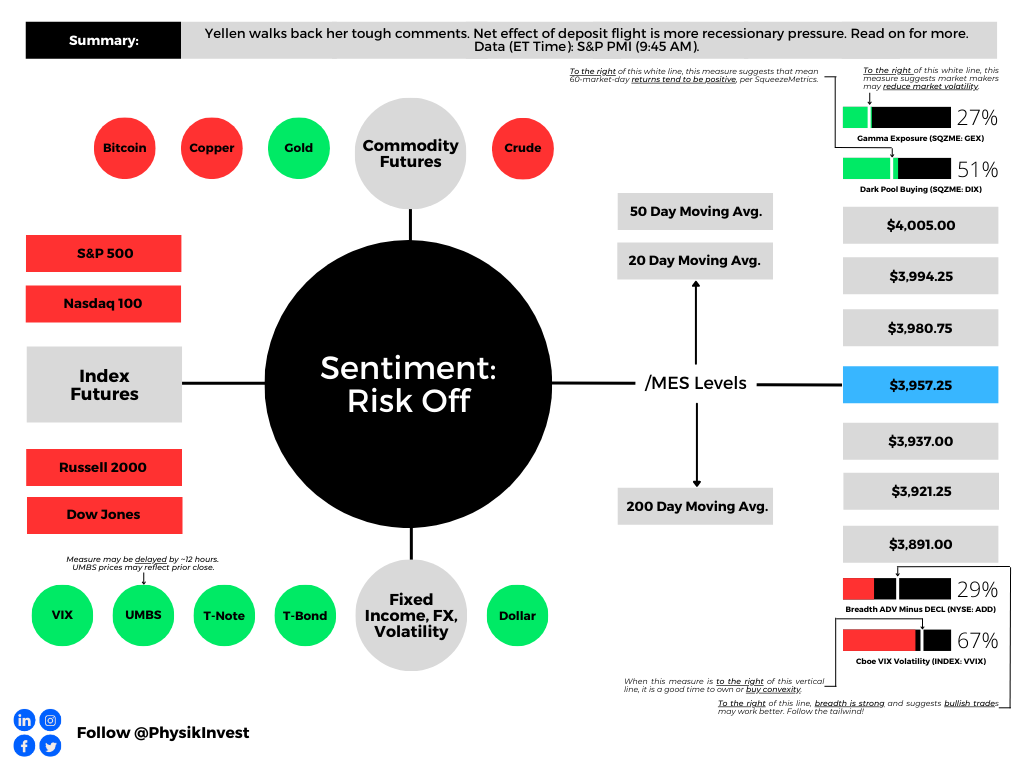
Good Morning! I hope you have a great start to the week. I would be so honored if you could comment and/or share this post. Cheers!
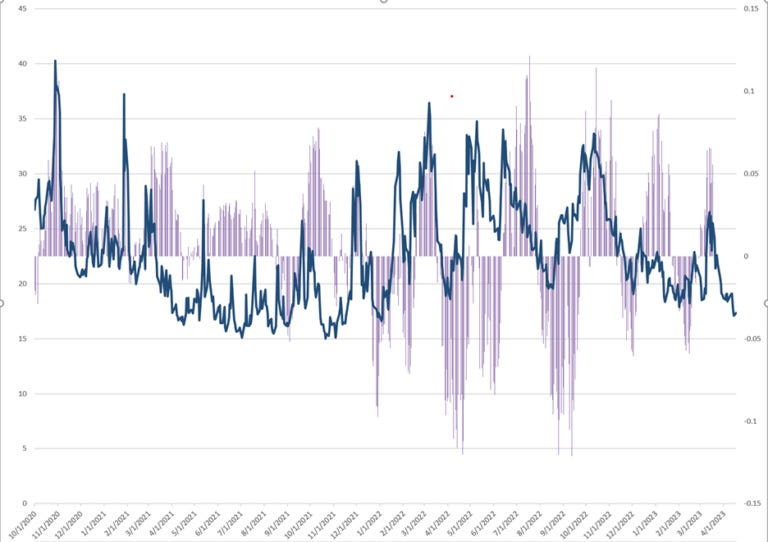
Bursts of volatility punctuate calm and resilience, resulting in demand for safety and protection in everything from stocks and commodities to bonds and currencies. The general agreement is that macroeconomic policy and geopolitics are to blame, and investors are repositioning to stem risk and potential bleeding in their portfolios. This sometimes disturbs historical trends and relationships.
Thank you for tuning in. We will unpack much of it herein. Let’s get into it.

Hedging Against Monetary Inflation, Weaponized Dollars, And Debt Monetization
Gold serves as a prime example. Instead of being guided by conventional catalysts, including real interest rates (i.e., nominal interest rate minus inflation), growth prospects, and currencies like the dollar, recent movements are more likely driven by factors like central bank accumulation on macroeconomic and geopolitical shifts.
For instance, China may increase its gold reserves to hedge potential disruptions and sanctions, as Russia saw after it invaded Ukraine in February 2022, or establish a collateral reserve for an autonomous financial system. Likewise, Poland, the Czech Republic, and Singapore have also increased their gold reserves.
As liquidity in the gold market is thinner, this buying activity amplifies volatility and disrupts established trends. Therefore, fast moves up!
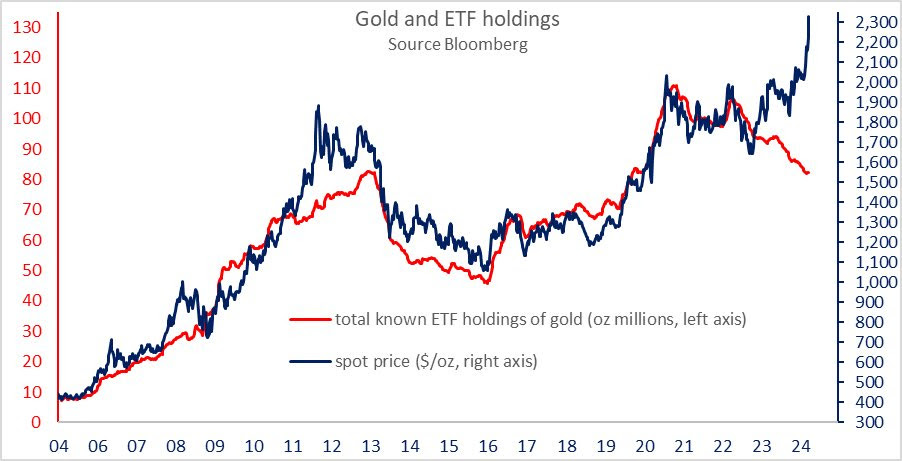
Why could gold continue this upward trajectory?
The typical trajectory is guided by monetary inflation, characterized by increasing liquidity within the financial system. According to CrossBorder Capital, gold moves 1.5 times the liquidity growth, a solid sensitivity to so-called monetary expansion. Bitcoin, often considered a digital gold, moves sooner and exhibits higher sensitivity.
Recent expressions of interest in Treasury securities by central banking authorities, such as Federal Reserve Governor Christopher Waller, further fuel ascents. New demand would lead to higher bond prices and lower yields.
Therefore, gold continues surging due to geopolitical shifts, liquidity in the financial system, and the potential for debt monetization. The latter occurs when excessive debts prompt central bank authorities to intervene, using printed money to purchase bonds to manage interest rate levels more effectively.
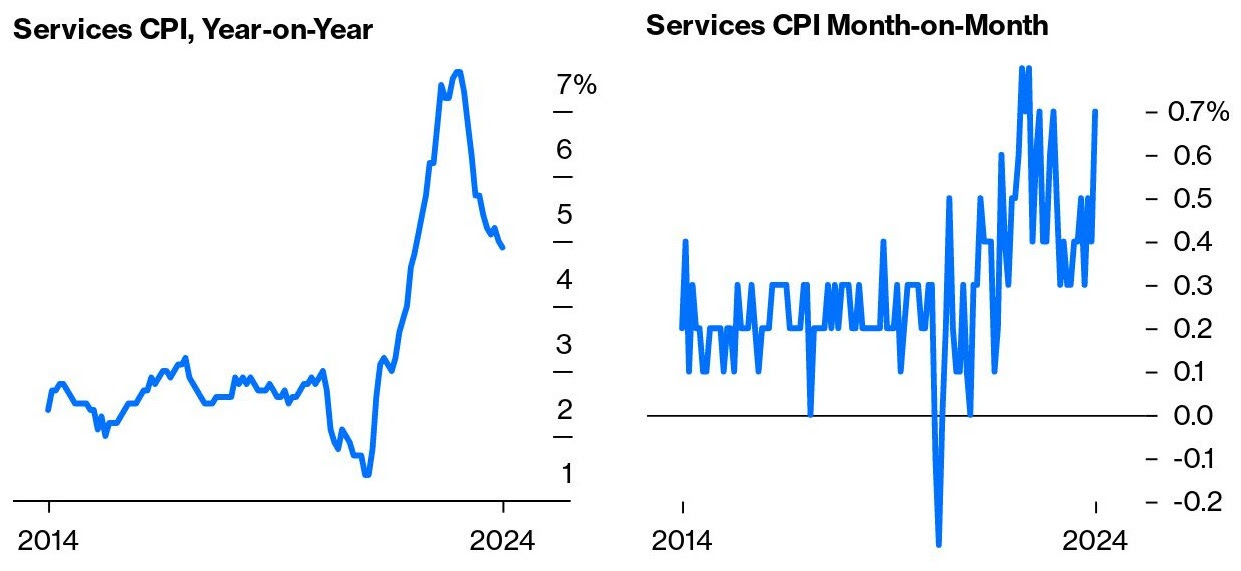
“Investors are looking beyond the ‘here and now,’ realizing that there is no way markets or the economy can sustain 5% nominal and 2% real rates,” Bank of America elaborates. Investors are “hedging two things: i) the risk that the Fed cuts as CPI accelerates, and ii) and more ominously, the ‘endgame of Fed Interest Cost Control (‘ICC’), Yield Curve Control (YCC) and QE to backstop US government spending.’”
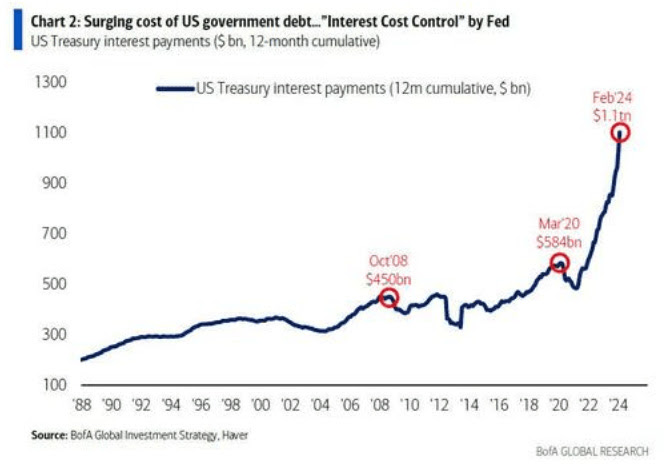
There is bi-modality. Typically, high rates are bad for gold. But, with debts and rates as they are, the probability of debt monetization increases. For now, we have a cycle wherein stocks and commodities may rise with a firming economy, and bonds may offer limited salvation, nodding to higher-for-longer rates.
Hedging Loss Of Momentum And Left Tails Following Big Move-Up And De-levering
Interest rate increases are likely only on the horizon if something unexpected occurs. Given that stocks are priced well, the question arises: how can we protect ourselves while many anticipate, based on market pricing, either minimal changes to the status quo or a substantial event triggering a broad downturn?
For one, commodities don’t do much good in a broad downturn.
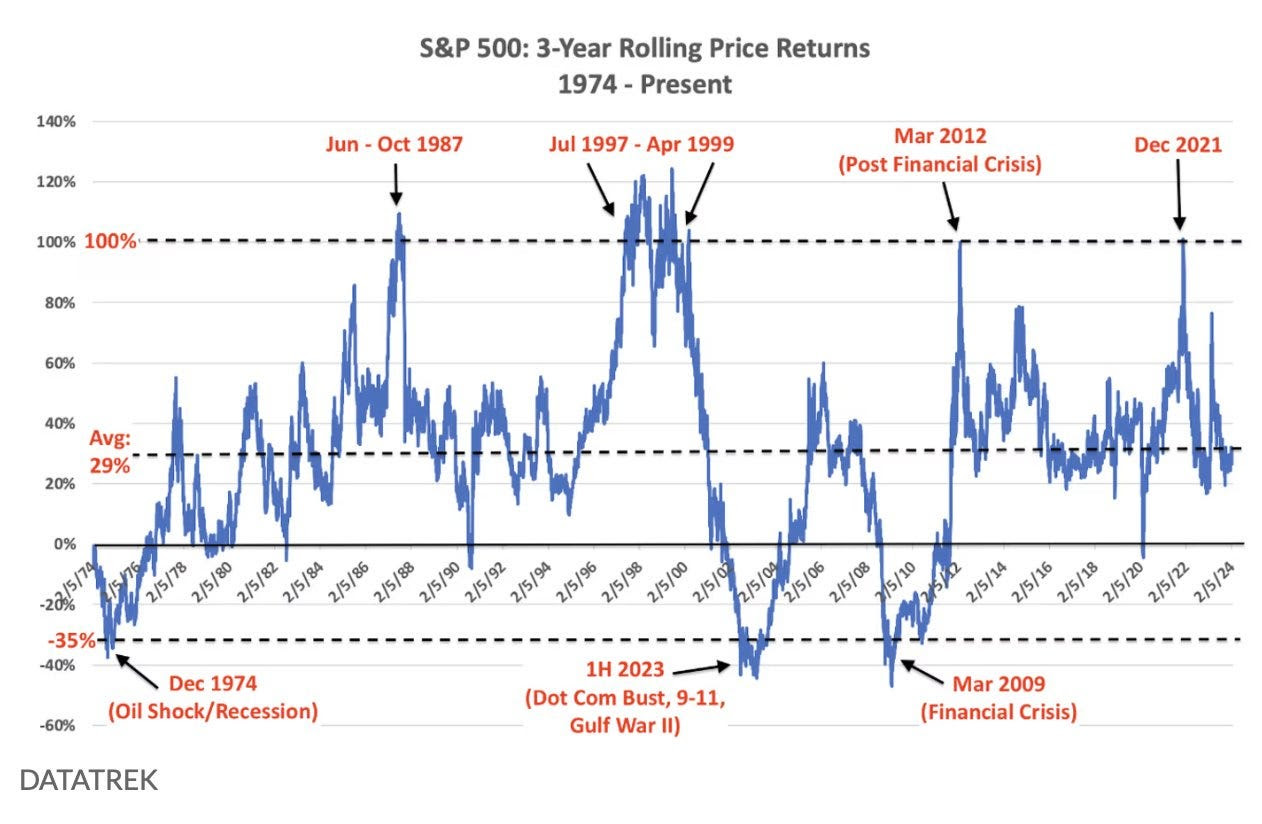
Consider the years 2001 (during the tech bubble), 2008 (amidst the global financial crisis), 2015 (the flash crash), 2018 (during Volmageddon), and 2020 (amidst the pandemic). According to Kris Sidial of The Ambrus Group, gold was an ineffective hedge against equities during these periods.
So, how do we hedge the middle reality between “minimal” and “substantial.”

While direct bets on equity volatility bursts have been prominent, digestion trades may be a better alternative. Let’s unpack why.
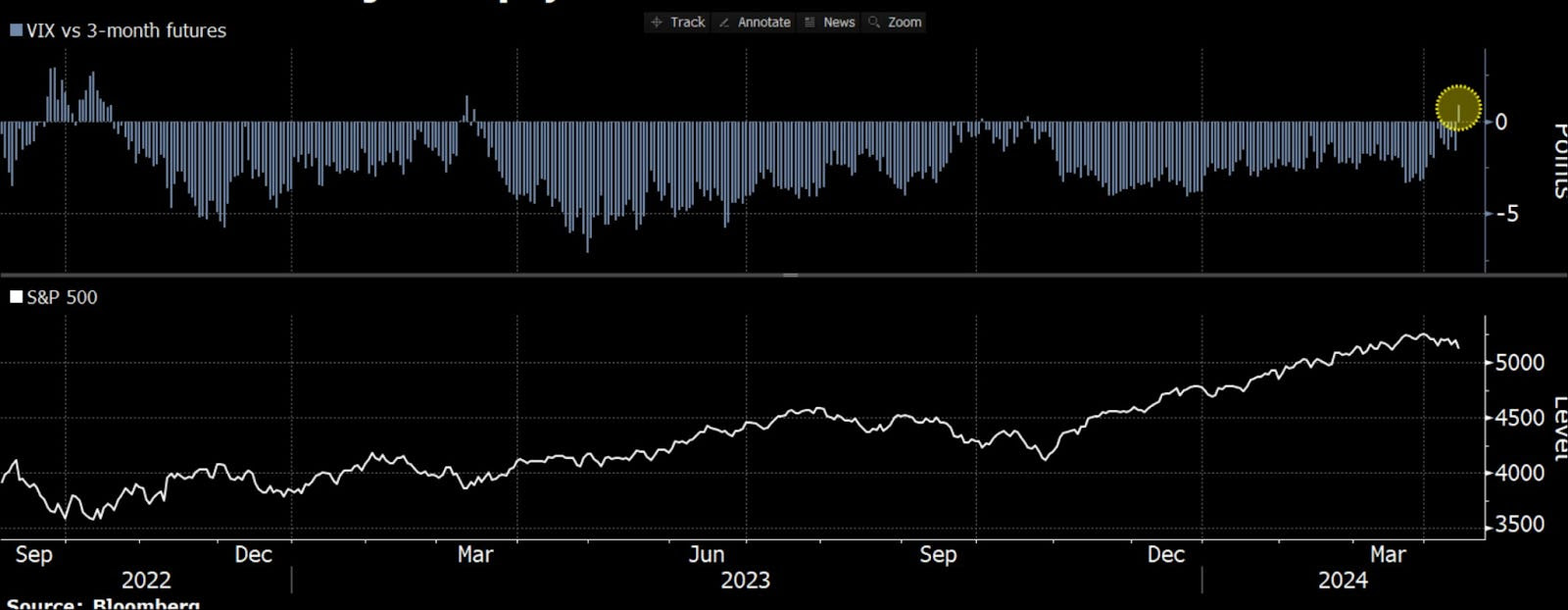
The first idea involves hedging downside thrusts in equities via call options in the Cboe Volatility Index (INDEX: VIX), Goldman Sachs, and UBS note. This isn’t necessarily optimal. Volatility is high over the short term and may revert quickly, indirectly boosting stocks. The alternative strategy entails selling options and utilizing the funds to purchase similar options with later expiration dates. Such digestion trades enable traders to capitalize on increases in volatility in the near term, reducing their costs on longer-term trades.

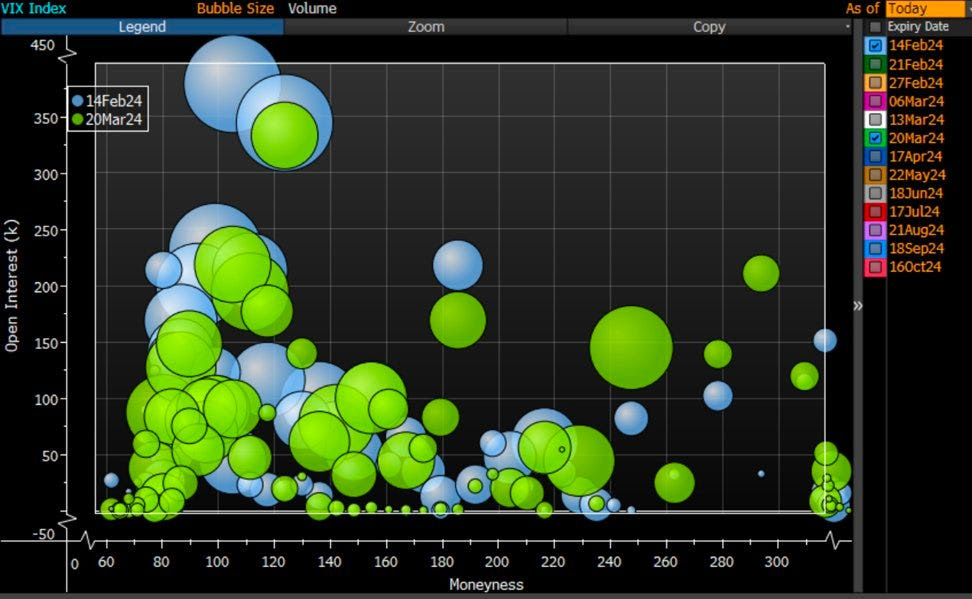
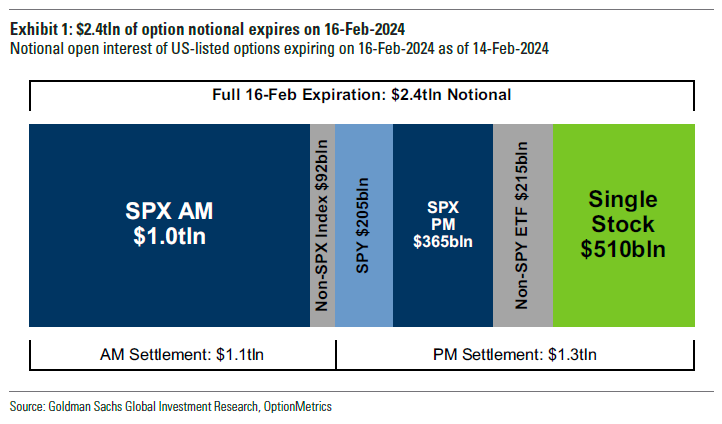
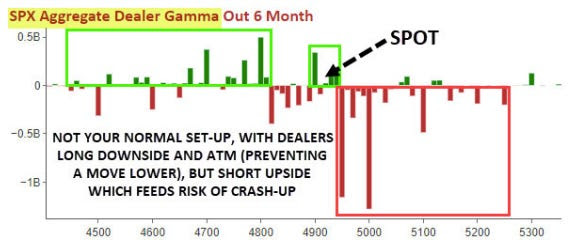
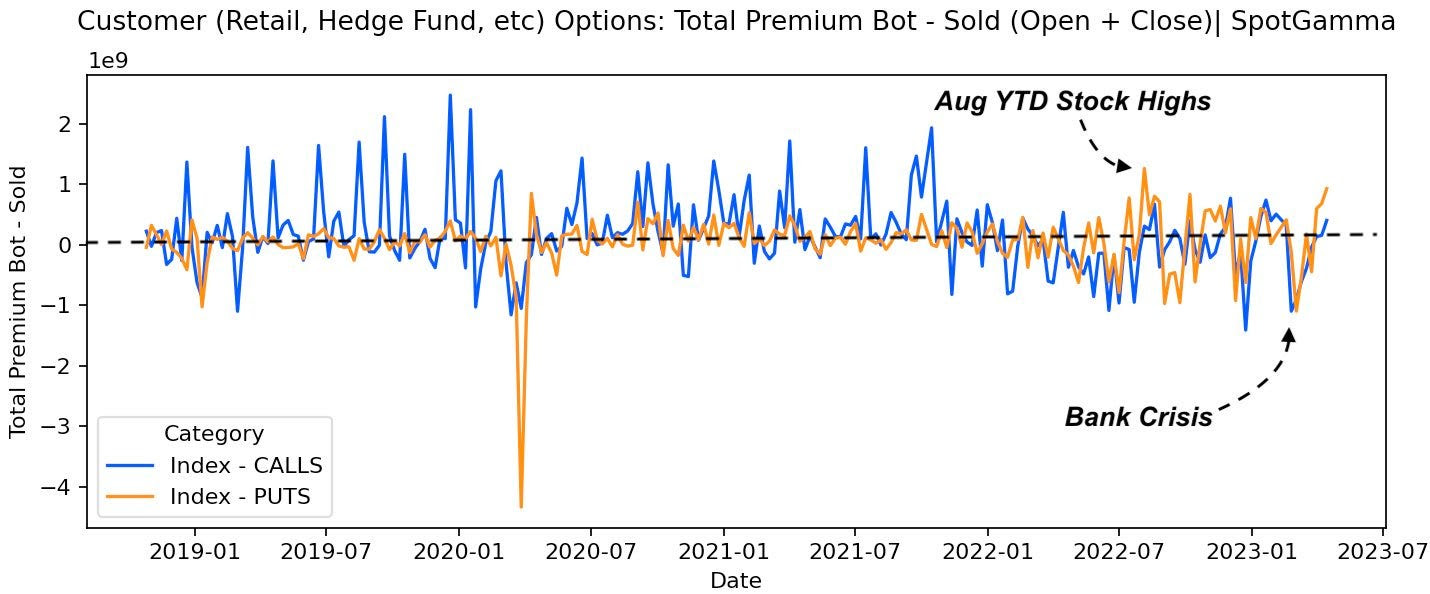
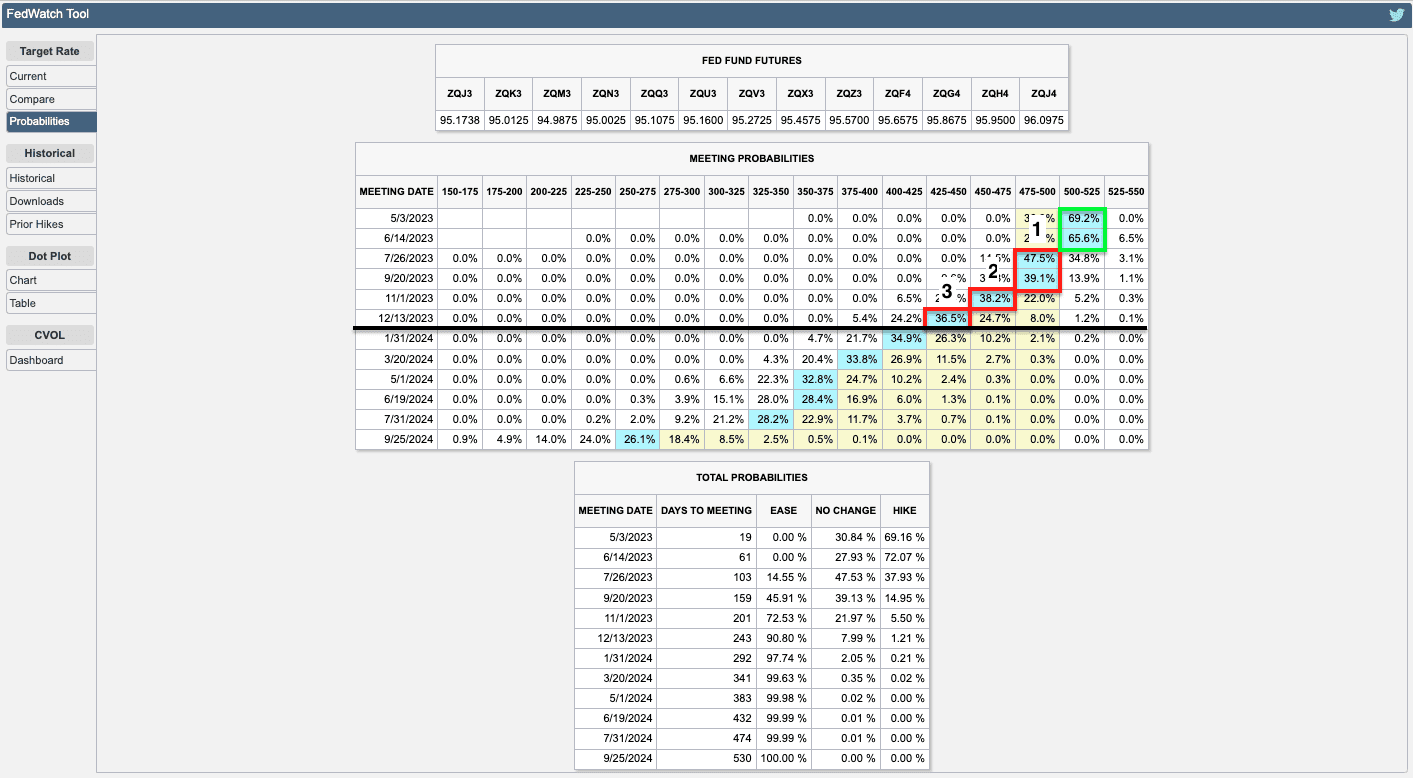
To explain, in a recent letter to subscribers, SpotGamma shared that numerous expiring VIX call options were in the money. In other words, this exposure, which makes money if the VIX and S&P 500 implied volatility (or the options market’s anticipation of future movement in the underlying), was soon to disappear. Accordingly, the hedges to this exposure would do the same, and the rebalancing after that would be enough to buoy markets.
We’ll try to break it down further in the simplest way possible.
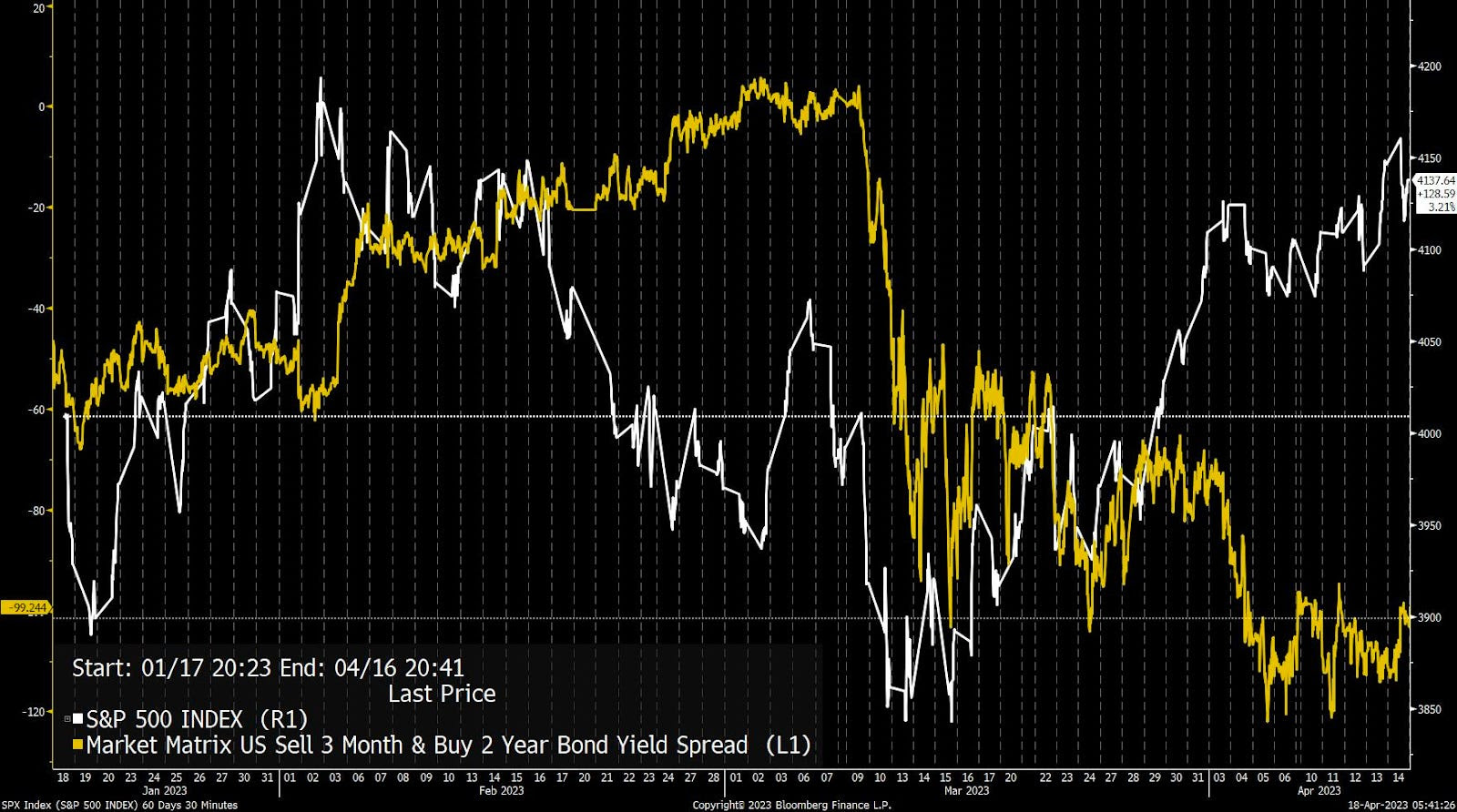
The S&P 500 (INDEX: SPX) and VIX are inversely correlated. When the S&P 500 falls, the VIX tends to rise. Naive of us to say, we know, but bear with us.
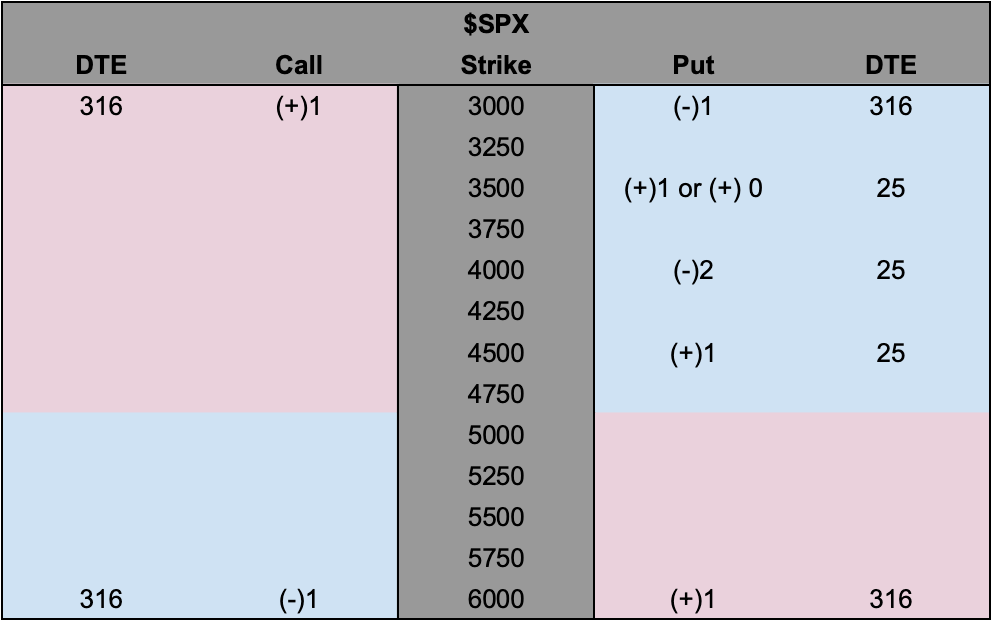
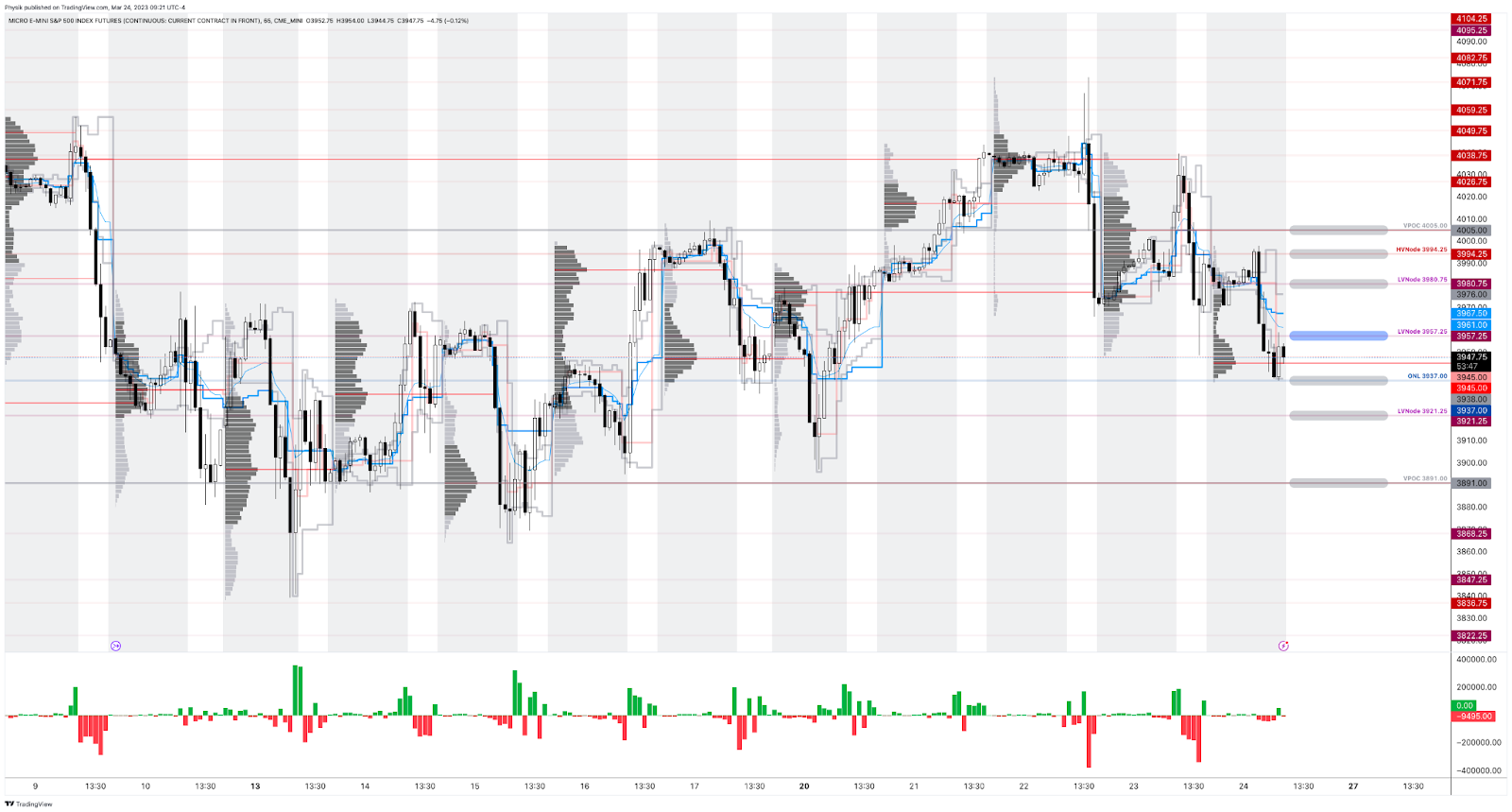
One can buy an SPX put or a VIX call to hedge a portfolio’s volatility. Let’s say one buys an SPX put, and the other side of this trade sells an SPX put. The other side may hedge this short put by selling stock and futures correlated to the S&P 500. Let us say the S&P 500 falls and volatility rises (pictured below). That counterparty may have to sell more stock and futures, pressuring markets. If this now valuable put expires, the counterparty will buy back the stock and futures it sold. This can support markets or do less to exacerbate movement and underlying volatility.

SpotGamma’s data suggests the markets are not facing an impending crash; instead, per their April 17, 2024 note, “if stocks rally and IV drops, it may add more stock for dealers to buy.” I plug SpotGamma because I worked there. Check them out! 

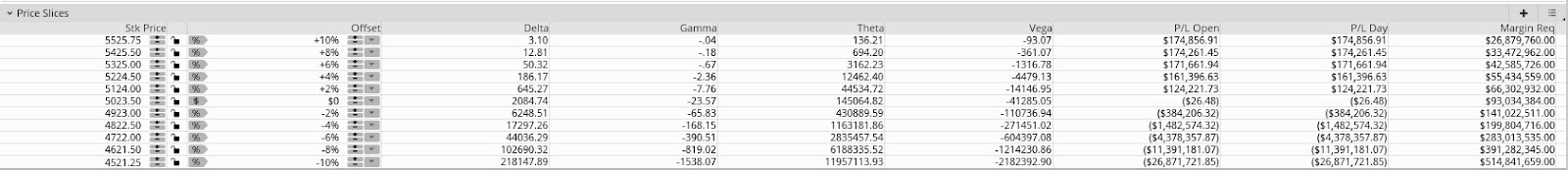
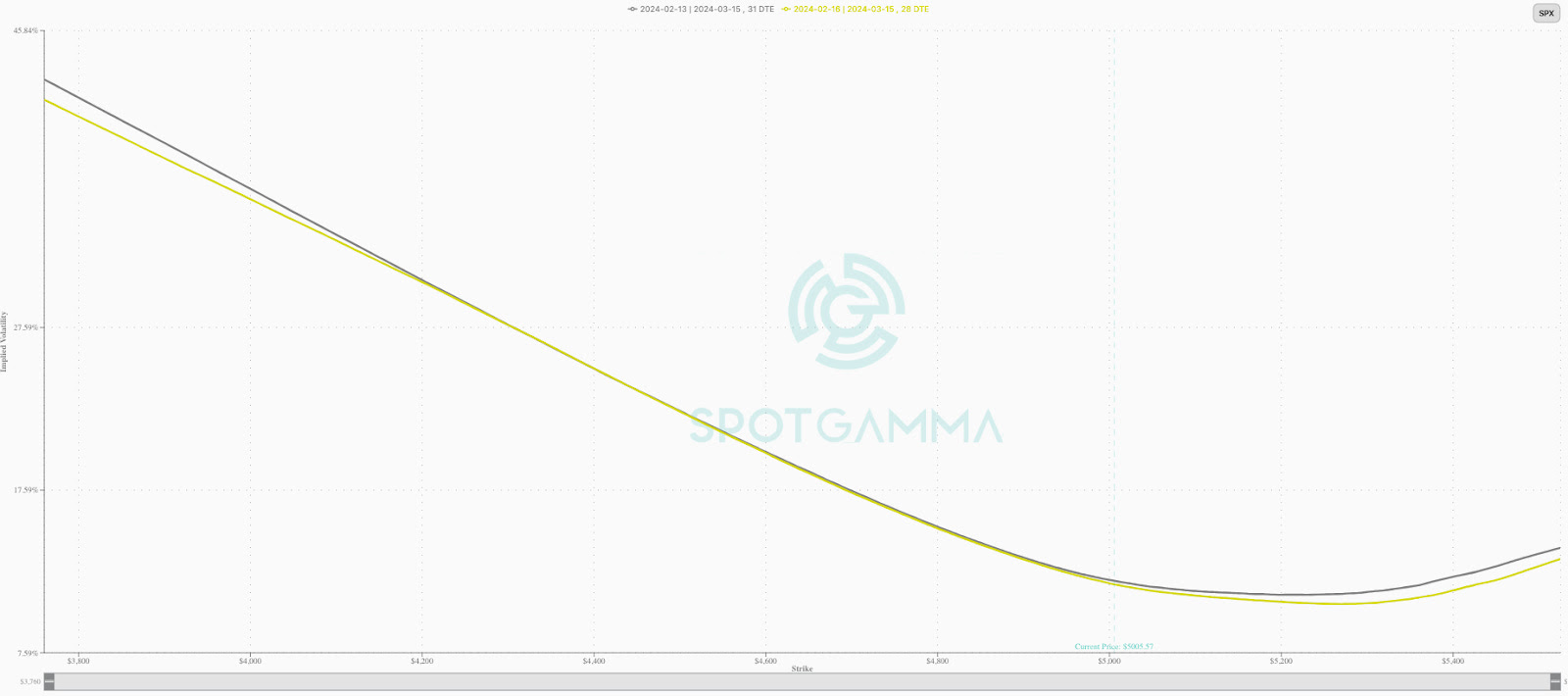
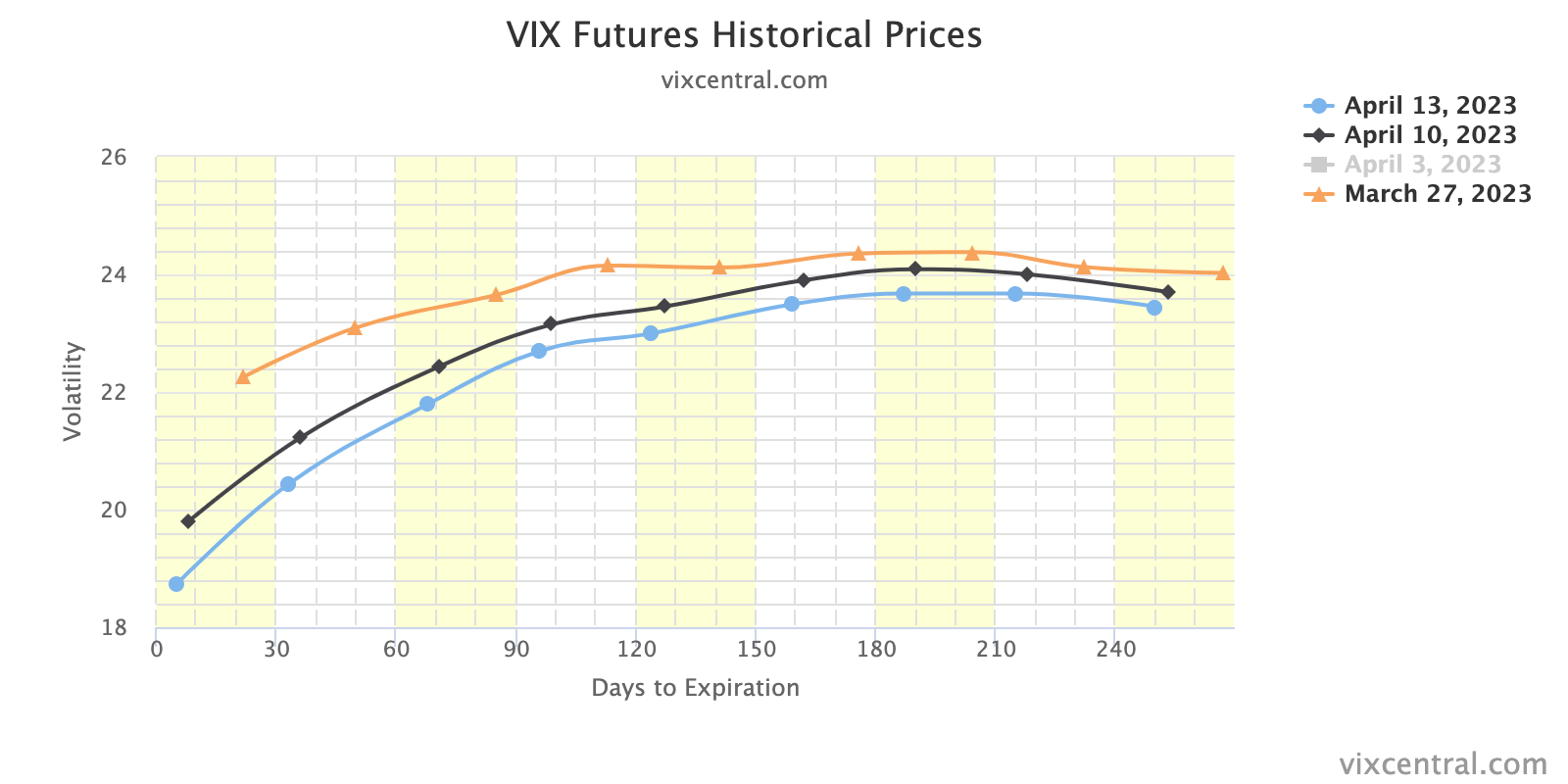
So, calendar and unbalanced butterfly or ratio spread trades (pictured naively below), a play on the recent richness (pictured much further above) of options, may help capture the low case of downside and stem potential portfolio volatility.

Flipping these trades (i.e., using call options in the SPX instead of put options) allows one to play the market rising. For instance, let us say the upside of gold and silver will continue, but only after stopping and digesting recent movements. You can sell a call expiring soon and buy one later at the same strike price. Your loss is, technically, limited to the amount paid for the trade.
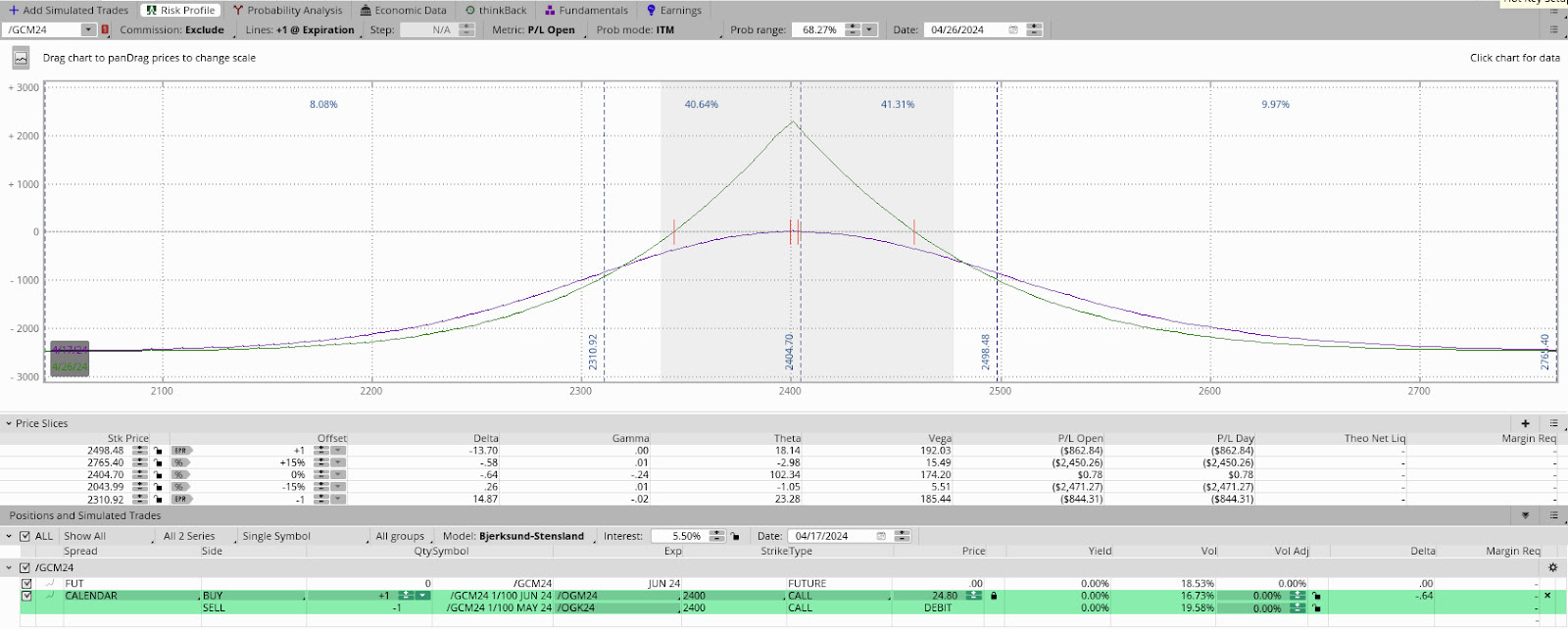
In general, ratio spreads, and butterfly trades are designed to capitalize on movement toward specific price levels, while outright calls and puts are better suited for hedging sharp movements.
The former two strategies serve as practical tools for safeguarding the value of your positions during periods of heightened volatility. In such environments, the options you own are positioned closer to the market, usually retaining their value well, while the options you sell are priced higher than usual and located farther from the market, with more value to decay into expiry.
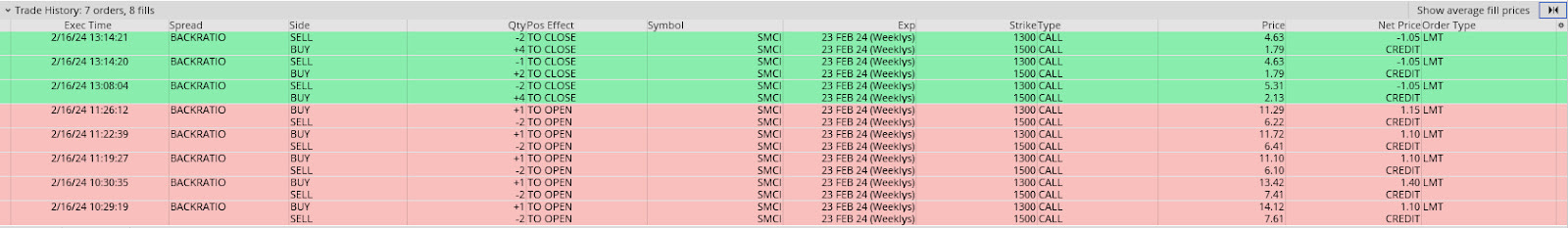
Consequently, while the options you own tend to keep their value, the options you sell struggle to retain theirs. As a result, the spread can appreciate even without significant movement, particularly if implied volatility declines significantly at the furthest strikes. Earlier this year, such was true in Super Micro Computer Inc (NASDAQ: SMCI) and Nvidia Corp (NASDAQ: NVDA).
SMCI was trending up, and traders were feverishly betting/hedging this reality. In a 20-page case study we may release, we detail how Physik Invest navigated this environment successfully. In short, we bought options closer to where the market was trading and sold more of them in places where we thought the market wouldn’t end up going. With implied volatility jacked, for lack of better phrasing, it was often difficult for those far-away and short-dated options to keep their value. Hence, we managed to put trades on for low or no cost and flip them for significant credits!!!

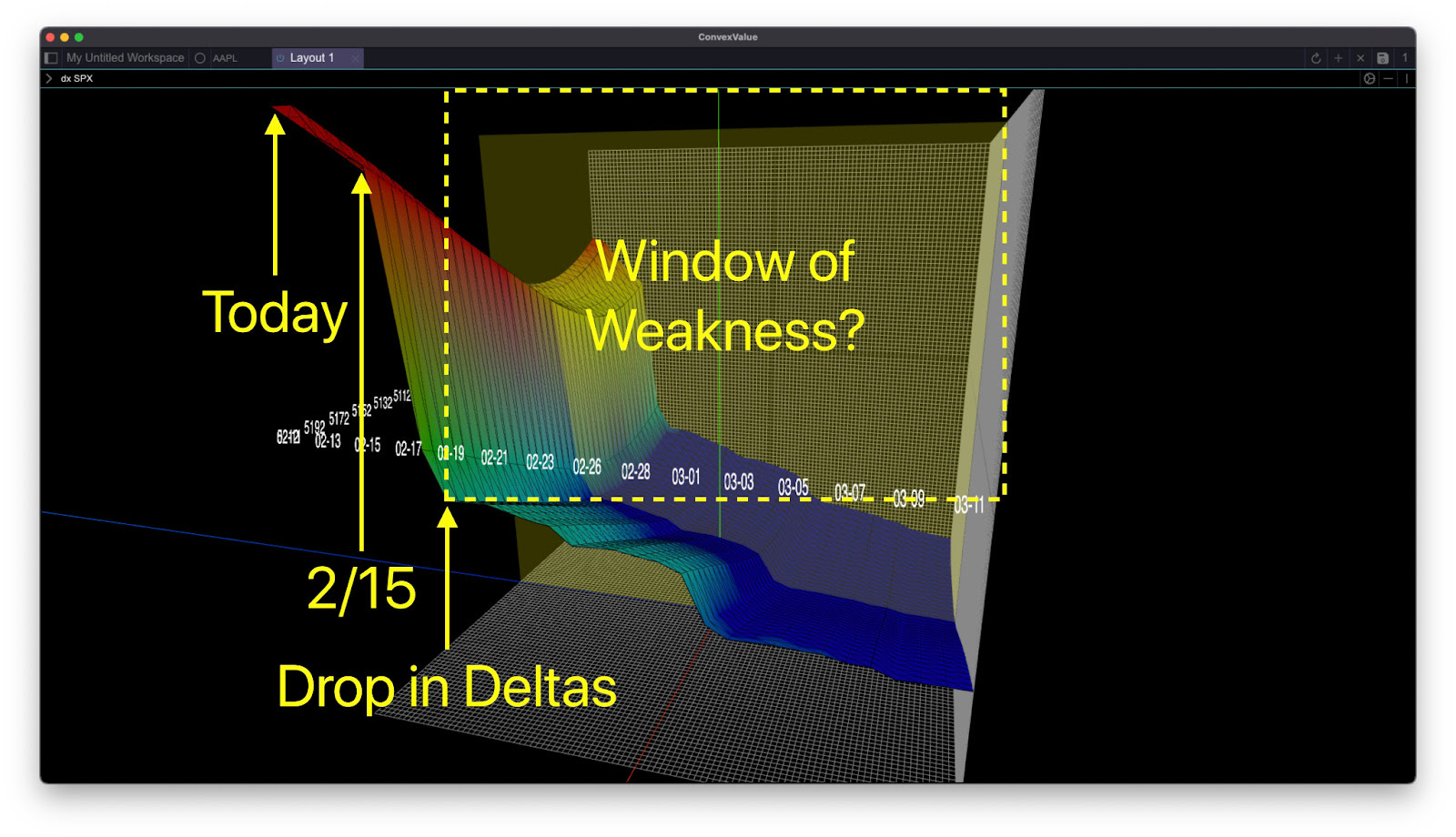
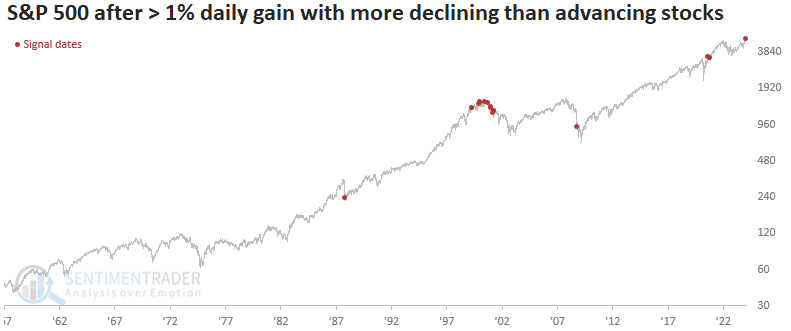
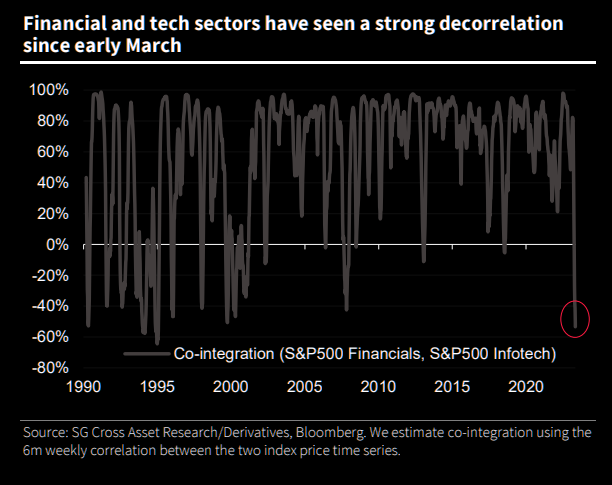
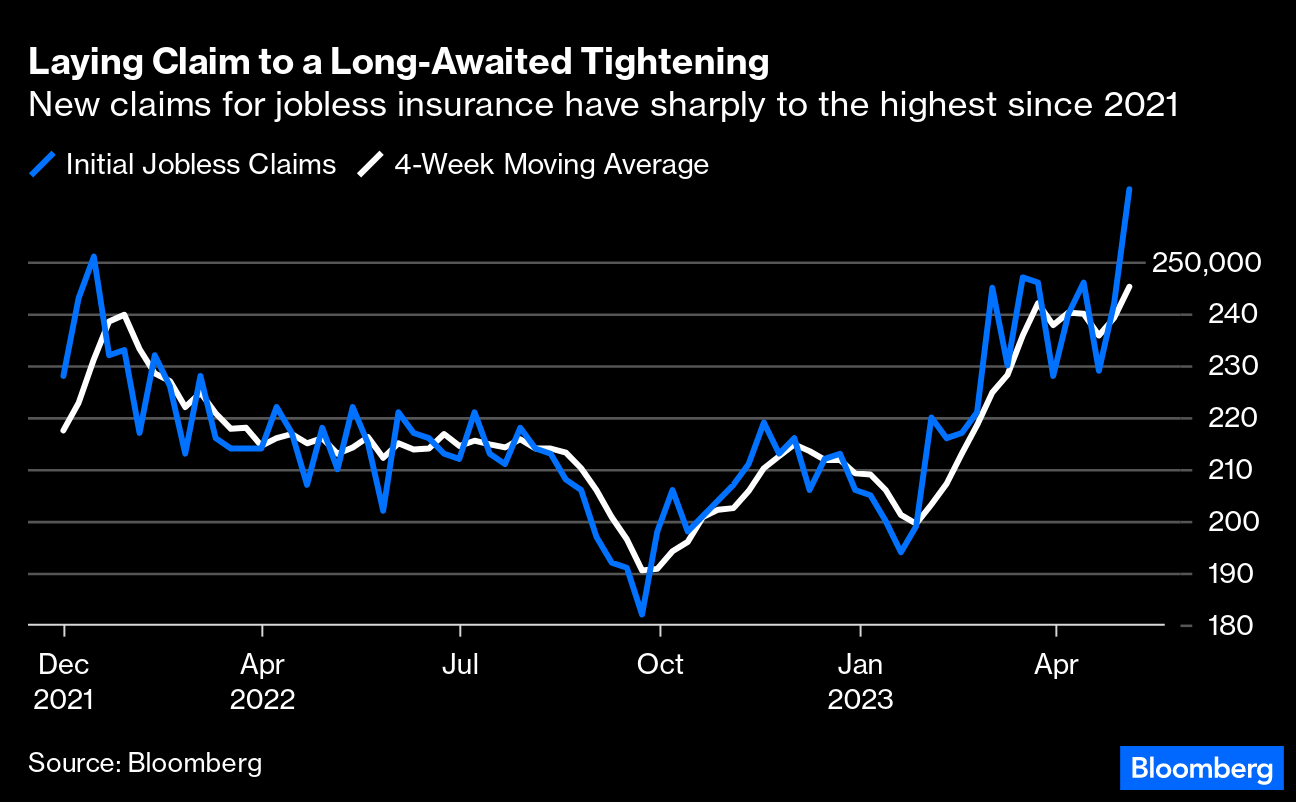
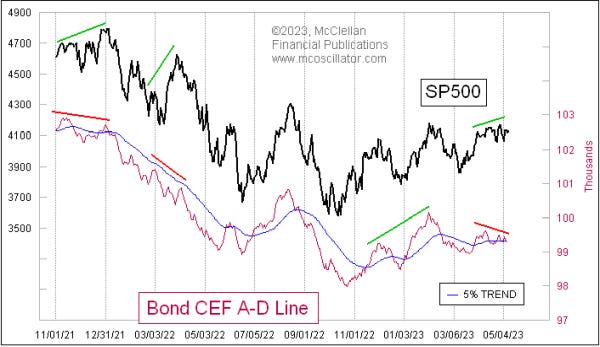
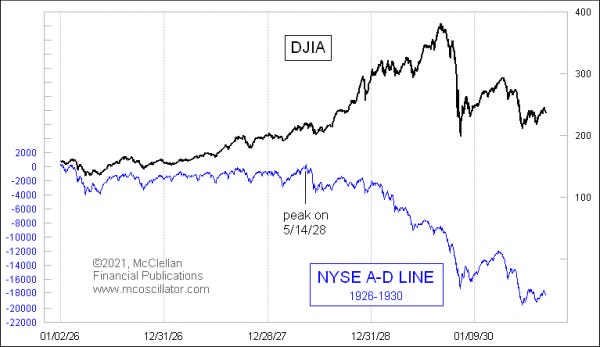
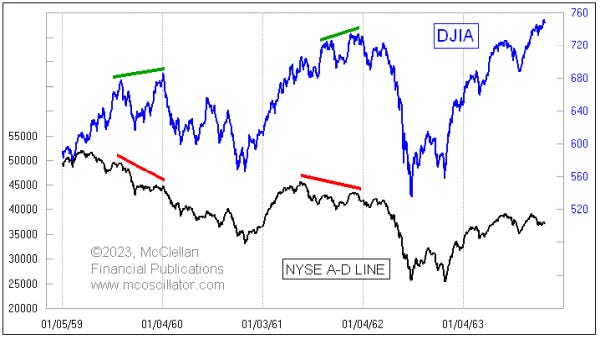
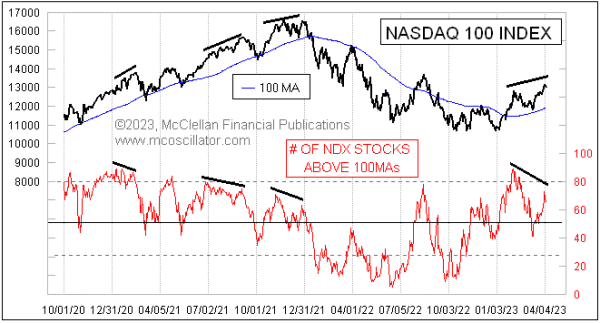
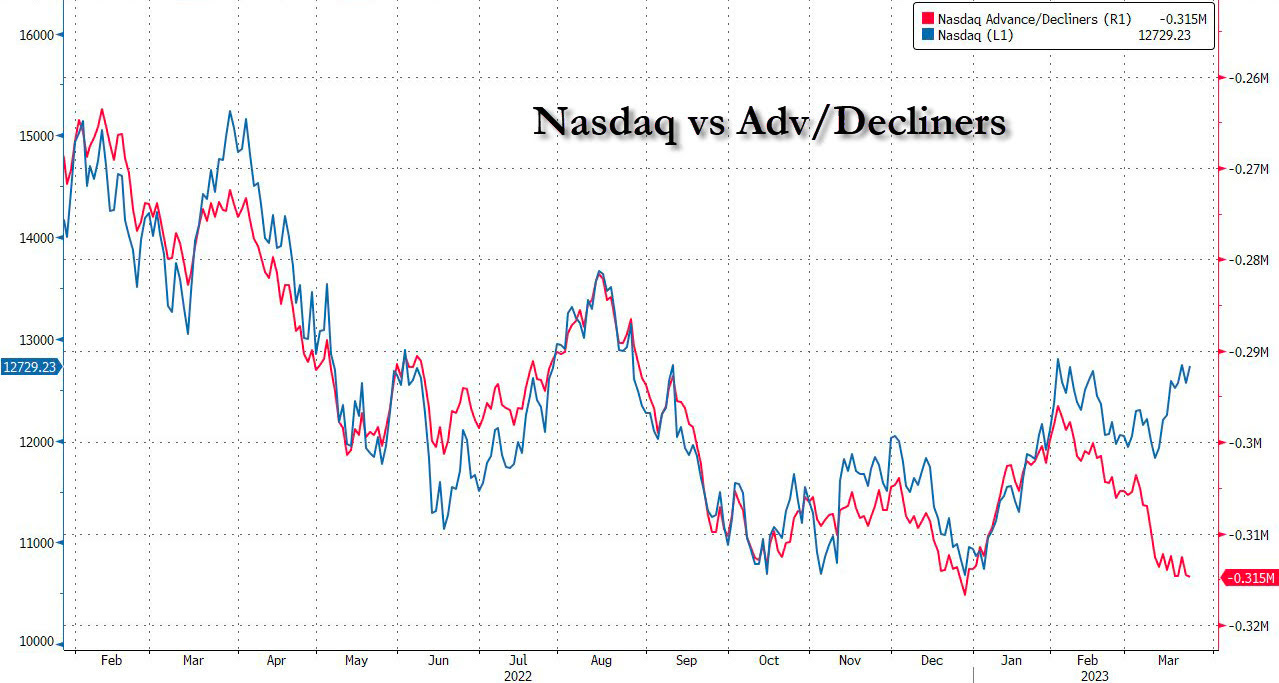
In any case, there’s been a weakening under the surface of the indexes (see below).
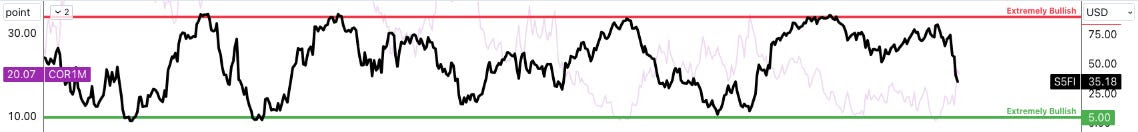
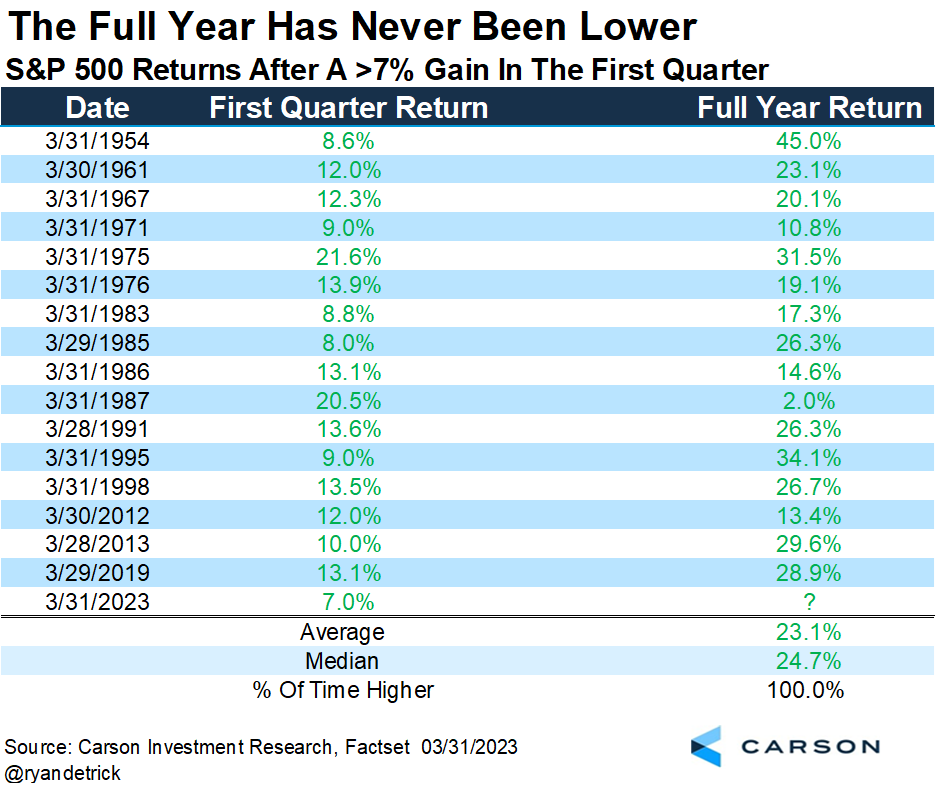
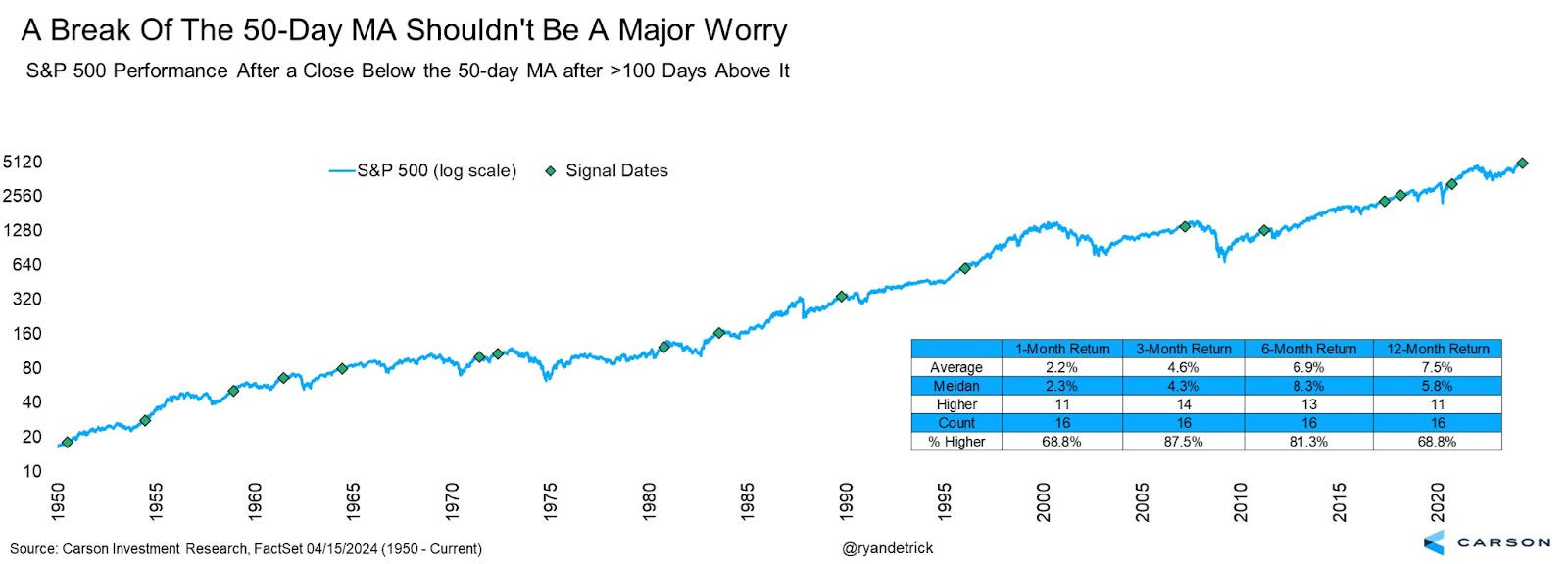
Later, when breadth improves, we can use the portfolio volatility-reducing trades discussed to cut costs or buy more stocks, anticipating upside continuation. According to Carson Group’s Ryan Detrick, the S&P 500 experienced its first close below the 50-day moving average in 110 trading days, marking the longest streak since 2011. Following similar streaks, stocks were higher three months later, 88% of the time, and six months later, 81% of the time. “A warning? Maybe, but maybe not.”
If you enjoyed this week’s letter, comment below and share. Thanks and take care!