“Good investing doesn’t come from buying good things, but from buying things well.” – Howard Marks
There is a lot of noise—it’s exhausting. Today, we will sift through the noise and focus on how we can protect and potentially grow our portfolios this year. This is a follow-up to our Market Tremors letter. But first, let’s clarify the context for our approach. This is a long newsletter, so you may have to view it in another window.
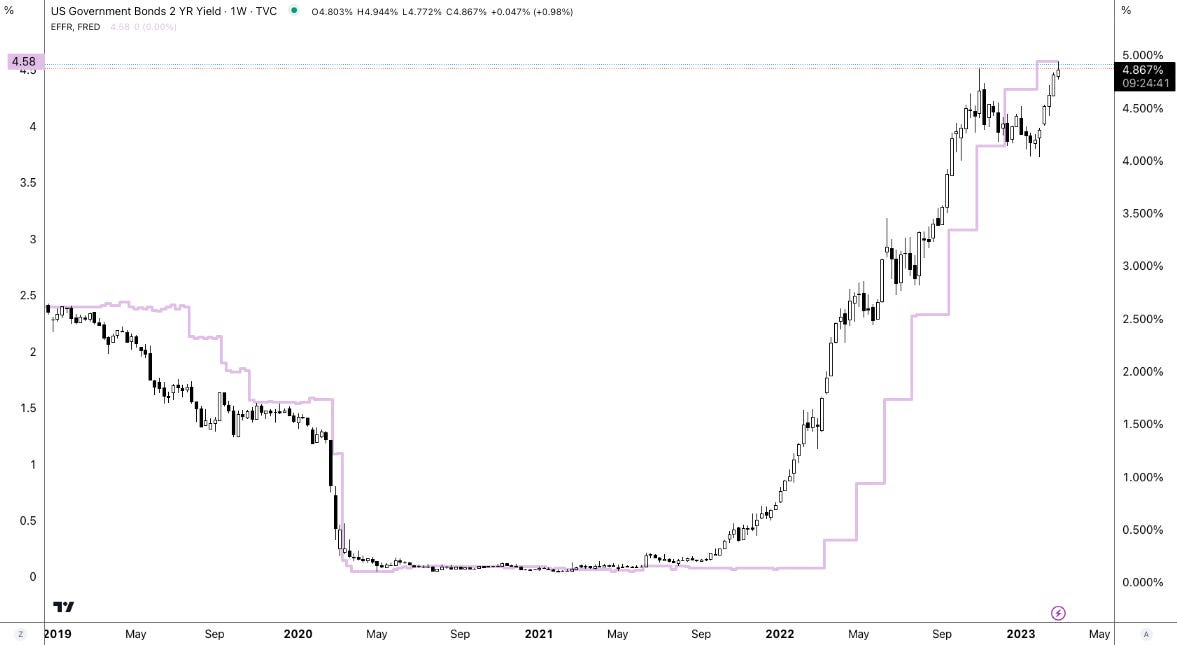
Inflation is back in focus, gold is soaring, and investors are optimistic about stocks. Correlations remain low, dispersion is high, and the market’s volatility pricing/positioning obscures potential risks lurking beneath the surface. The macro landscape is shifting rapidly, yet when we zoom out, we’re confronted with something we’ve discussed before: inflation is here to stay!
For a long time, the expectation was that inflation would take a particular shape—a transitory spike and a manageable trend. Instead, structurally, we’re dealing with a world that is moving away from the low-inflation paradigms of the past. The pillars supporting cheap capital and abundant liquidity—globalization and dovish monetary policy—are shifting.
These shifts are neither sudden nor unexpected. In 2023, we wrote much about the narrative of the ideological struggle between the West and East, particularly with the Russia-Ukraine conflict sparking. Historically, whenever Eastern economies prosper, the West adjusts the rules. Now, it’s more about who controls what. Control over assets, inflation, and interest rates define economic power. Folks like Zoltan Pozsar have warned that the fundamental drivers of the low-inflation era—globalization and financialization—are unraveling, leaving policymakers with little choice.
The well-respected Kai Volatility’s Cem Karsan, a mentor to many, has pointed out in excruciating, albeit digestible detail that the trends favoring high-beta portfolios over the past four decades are reversing. Monetary authorities, particularly the Federal Reserve, have been constrained in their ability to address the widening wealth divide. Their response to inflation in the early 2020s—from creating demand to absorb surplus supplies of low-priced items to structurally restricting demand in response to shortages—was intended to guide the economy along a path of managed declines in activity while maneuvering interest rates to prevent another inflationary flare. Rising populism is a byproduct manifesting as shifts in public demand and political sentiment.
Thus, today’s Mar-a-Lago Accords and the broader economic overhaul signify a significant trade, monetary policy, and financial stability restructuring. Tariffs, a U.S. sovereign wealth fund, and global security restructuring are the key issues at this forefront. The implications of this shift are profound, and markets have yet to adjust. A portfolio for this new environment could creatively layer exposure to stocks, bonds, commodities, and volatility. Understanding the pieces herein will be critical for structuring trades and managing risk. Let’s dive in.
Macro Context: A New Economic Framework
#1 – Tariffs
One significant component of this broader economic overhaul is tariffs. Economist Stephen Miran, nominated by the U.S. President to be Chairman of the Council of Economic Advisers, has outlined how tariffs, historically used to influence trade flows, are being retooled as protectionist instruments and an alternative revenue source.
According to Miran’s A User’s Guide to Restructuring the Global Trading System and fantastic explanations by Bianco Research founder Jim Bianco, a core issue is a persistently strong dollar distorting global trade balances. If paired with currency adjustments, tariffs could redistribute the costs away from U.S. consumers, “present[ing] minimal inflationary or otherwise adverse side effects, consistent with the [U.S.-China trade war] experience in 2018-2019.” However, this approach risks retaliation or distancing from key trading partners, further fracturing global supply chains.
To mitigate these risks, policymakers consider implementing tariffs in phases, gradually increasing rates to address inflationary pressures and market volatility. Even during the 2018-2019 trade war, tariff rate increases were implemented over time. Additionally, tariffs will be driven by national security concerns, targeting industries essential to defense and technological innovation. From this perspective, policymakers view access to the U.S. market as a privilege.
#2 – Sovereign Wealth Fund
A significant consideration is a U.S. sovereign wealth fund leaning on undervalued national assets to restore fiscal stability. Unlike traditional sovereign wealth funds built on surpluses, this fund would operate by revaluing and monetizing domestic reserves.
Key assets under consideration include undervalued gold reserves and billions in government-possessed bitcoin, which could be integrated into this fund. Bianco says these could total nearly $1 trillion.
This strategy introduces volatility concerns. Those concerned say government exposure and potential speculation on financial assets could lead to instability. Should we invest now for later?
#3 – Global Security Agreements
Beyond trade and monetary policy, a core element of the broader economic overhaul is linking military alliances to economic policy. The longstanding framework in which the U.S. provided security to allies without direct compensation is being rethought. The warnings are explicit; note the President’s Davos remarks and the Vice President’s Munich Security Conference speech.
Under a new paradigm, Bianco summarizes that NATO members may be required to contribute more to defense (say ~5% of GDP), foreign-held U.S. Treasury bonds may be converted into 100-year zero-coupon bonds, reducing short-term debt burdens, and tariff structures may be adjusted based on a country’s alignment with U.S. security interests.
“What Miran said in his paper is: you owe us so much for the last 80 years that what we want to do is a debt swap,” Bianco explains how the U.S. can be paid for being the world’s protector. “Those NATO countries have trillions of dollars of debt. [You’ll] swap it for 100-year or perpetual zero coupon non-marketable Treasury securit[ies]. So, you’re going to swap $10 billion worth of Treasuries for a $10 billion coupon century bond [that] won’t mature for 100 years, [and] won’t get any interest.”
In short, this is a fundamental shift that requires allies to bear a more significant share of security and costs. It’s the Mar-a-Lago Accords, a new financial order and policy framework akin to past agreements that reshaped the global economy, such as the Bretton Woods Agreement of 1944, which established the U.S. dollar as the international reserve currency, and the Plaza Accord of 1985, which coordinated currency adjustments to correct trade imbalances.
The proposed Mar-a-Lago Accords aim to reprice U.S. debt through asset monetization, weaken the dollar to improve U.S. export competitiveness and enforce tariff structures to rebalance global trade.
Positioning Context: Market Positioning Obscures
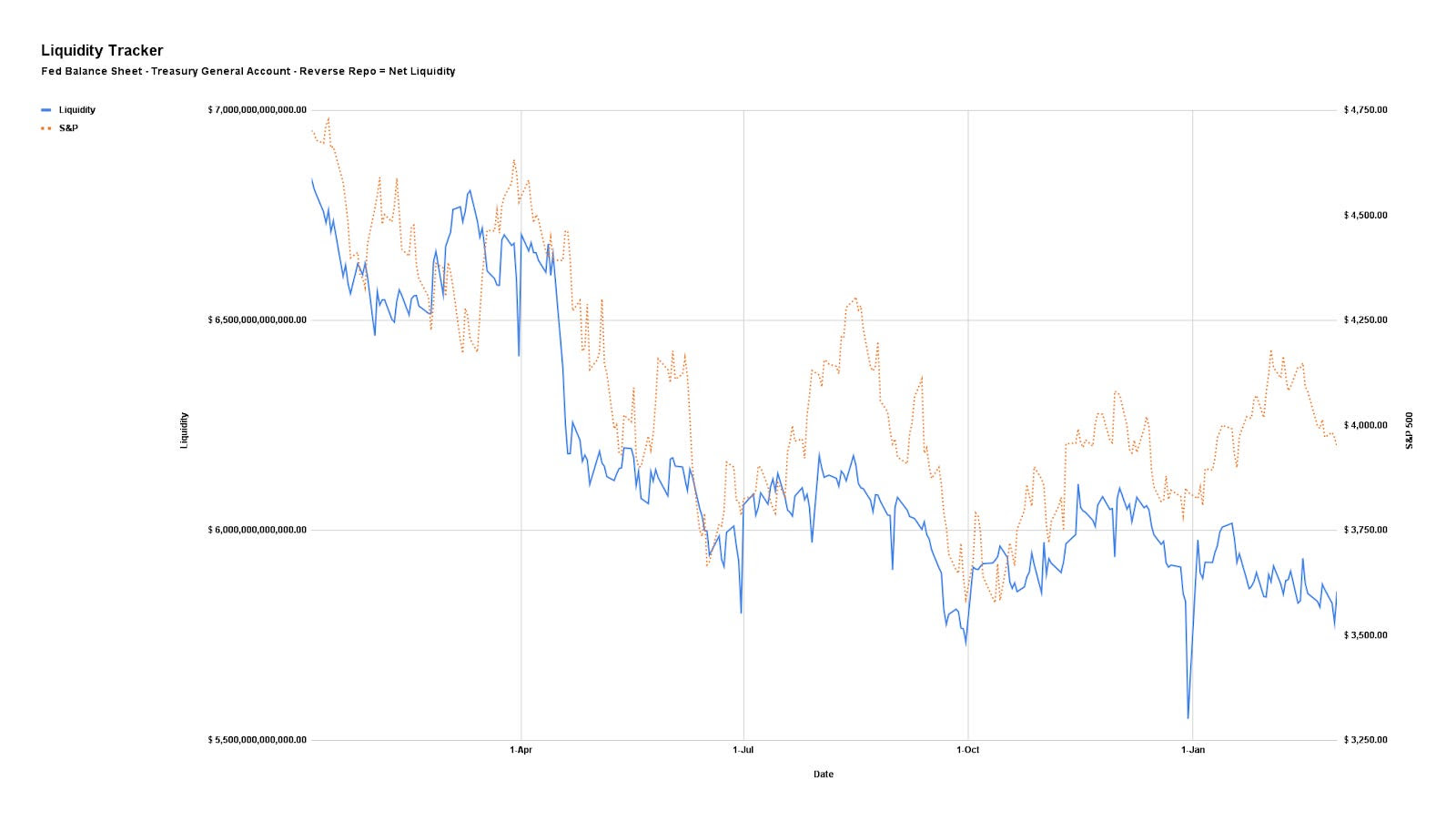
Tariff-driven price pressures, a weaker dollar, and a floor under interest rates raise bond yields, corporate borrowing costs, and strain leveraged players. This backdrop favors debasement plays and perceived safe havens like bitcoin and gold, which have been climbing for reasons discussed in the past and present.

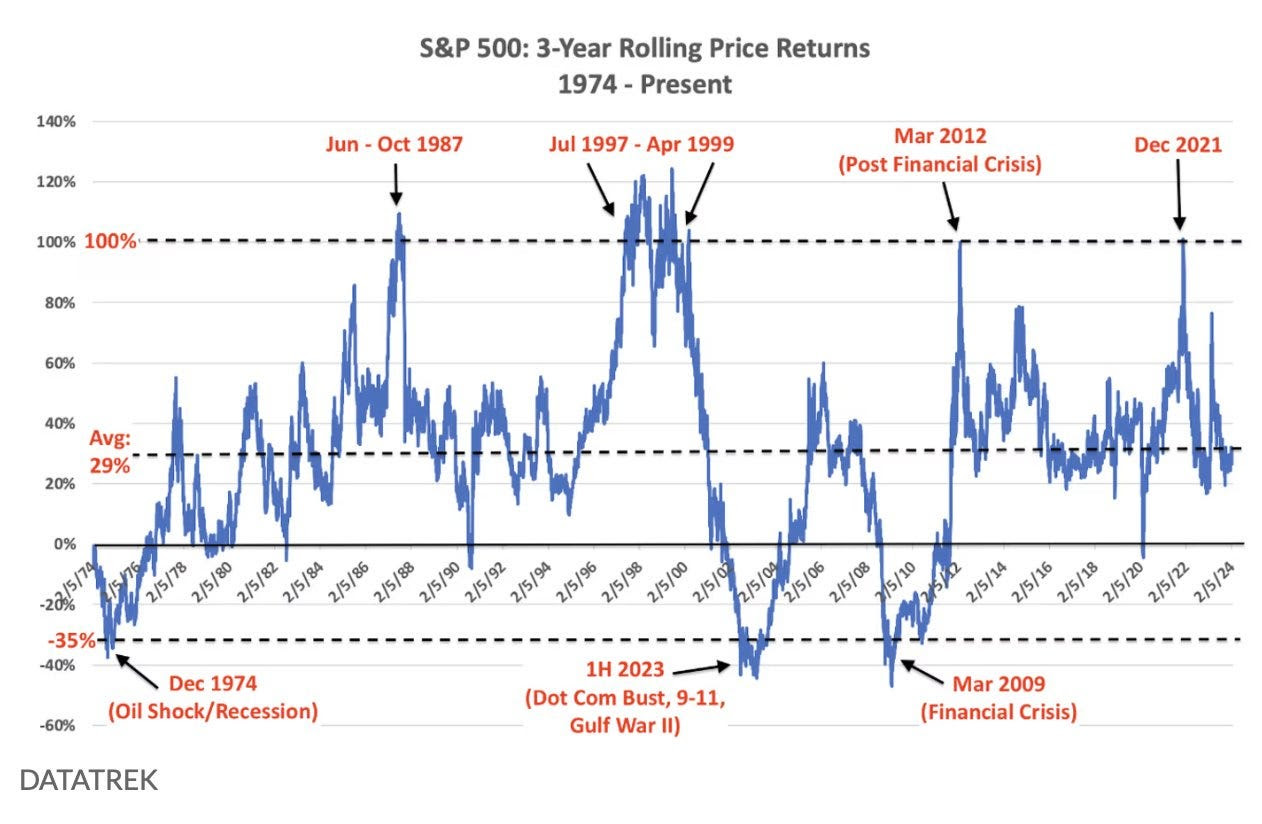
Equities face a less promising outlook. Oaktree Capital highlights that decade-long returns have historically been lackluster when investors bought the S&P 500 at today’s multiples. As Howard Marks puts it, earning +/-2% annually isn’t disastrous—but the real risk lies in a sharp valuation reset, compressed into just a few years, much like the brutal selloffs of the 1970s and 2000s.

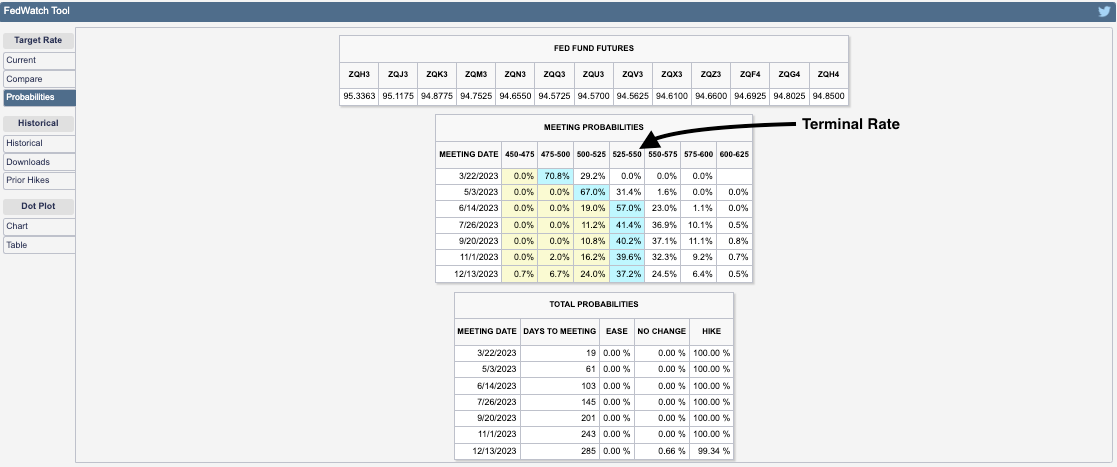
While the current market environment may feel frothy, with stretched valuations and narrow leadership, we’re not in an imbalanced 1970s scenario. Also, the possibility of a dollar devaluation serves as a tailwind for S&P 500 earnings, potentially boosting stock prices, Fallacy Alarm explains. Markets are not irrational; instead, they could face modest returns of around 5-6% annually for stocks and bonds over the next decade. Such sanguine sentiment is evident in the options/volatility market, reflecting the distribution of future possible outcomes; the trading and hedging of options make them a robust gauge of future outcomes—offering a view of where markets stand and where they might be headed.

We observe several key happenings:
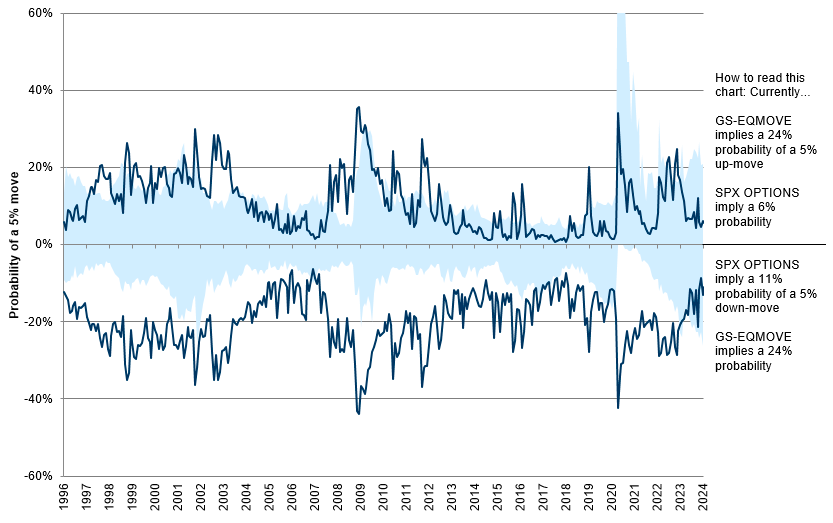
#1 – Hedging Volatility Spikes, Not Market Crashes
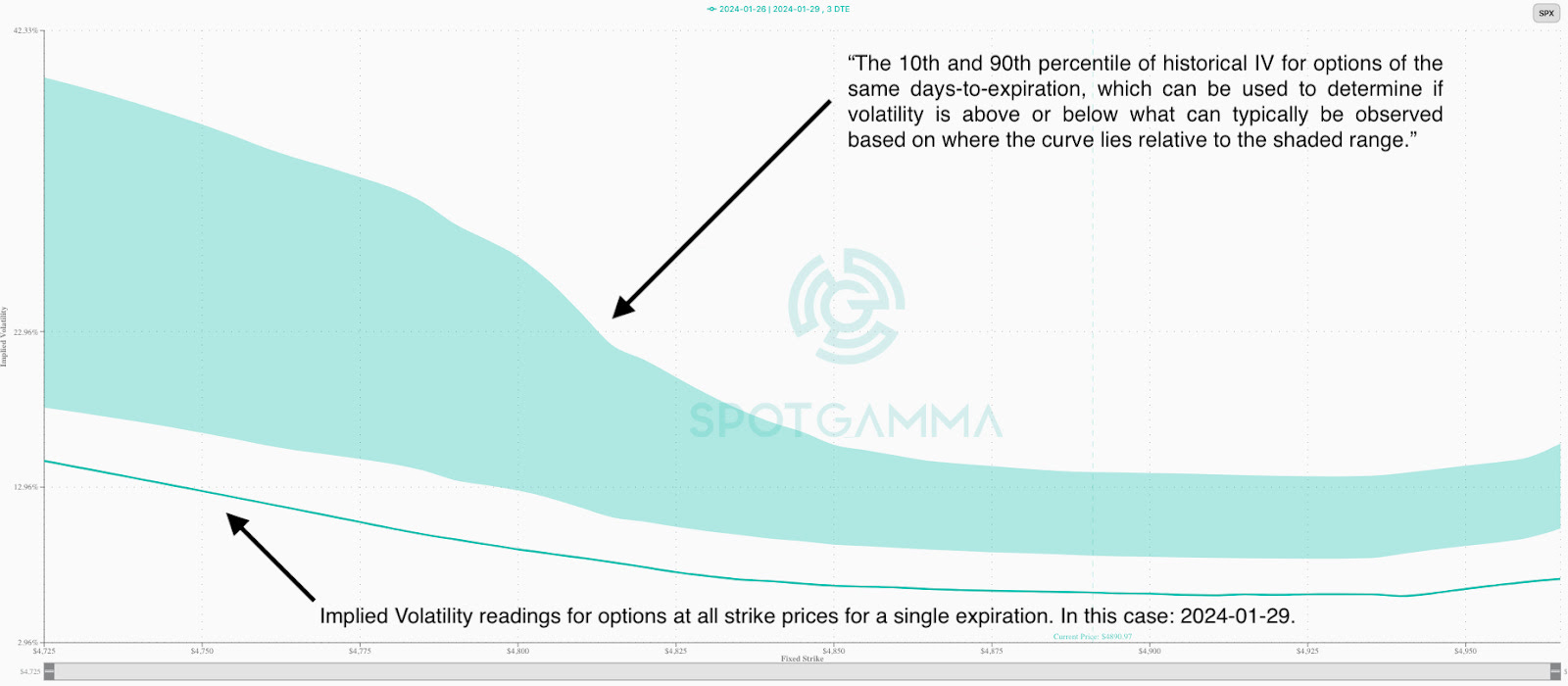
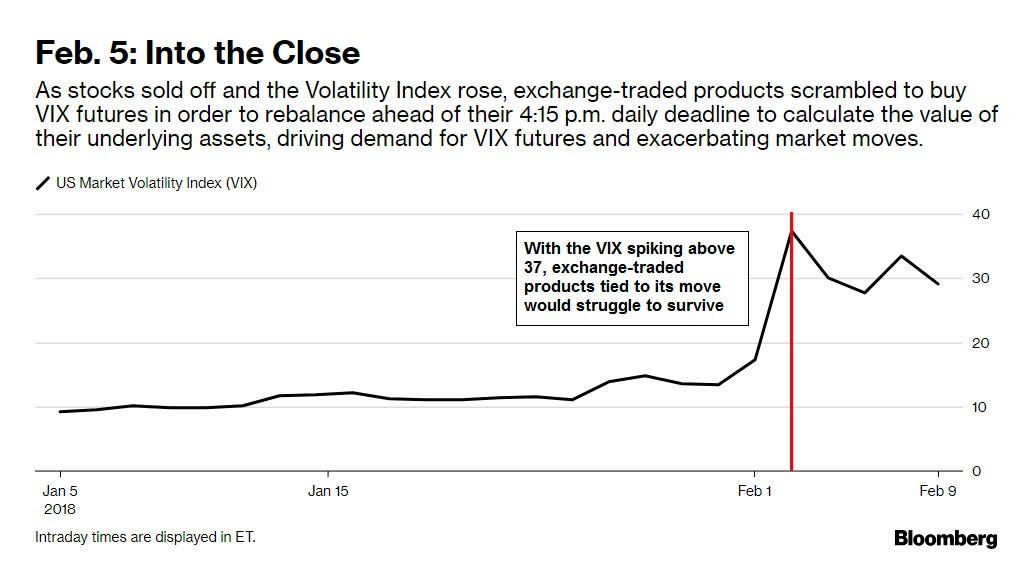
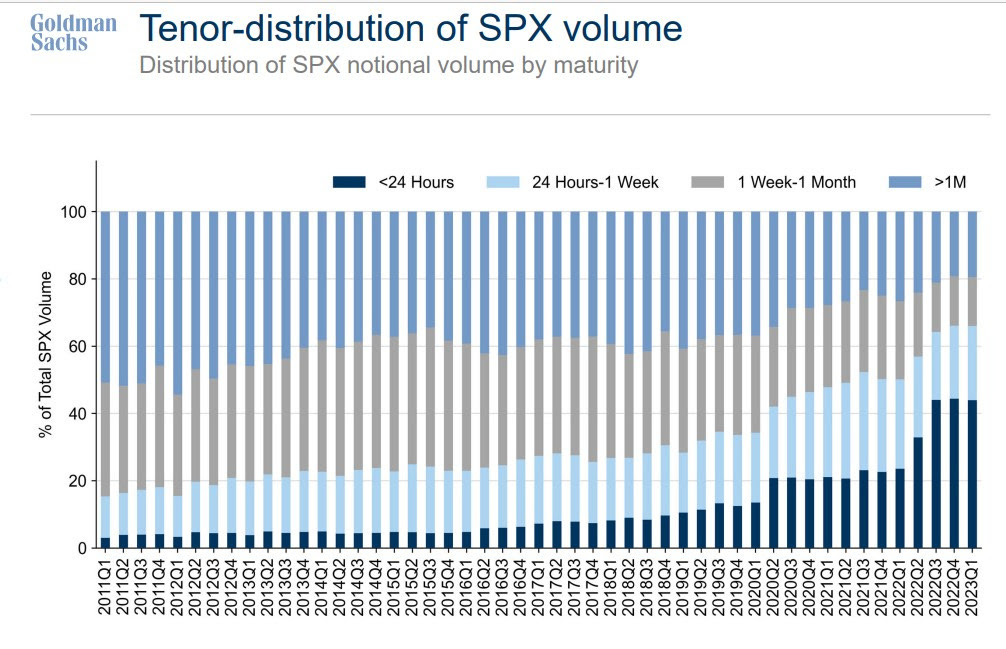
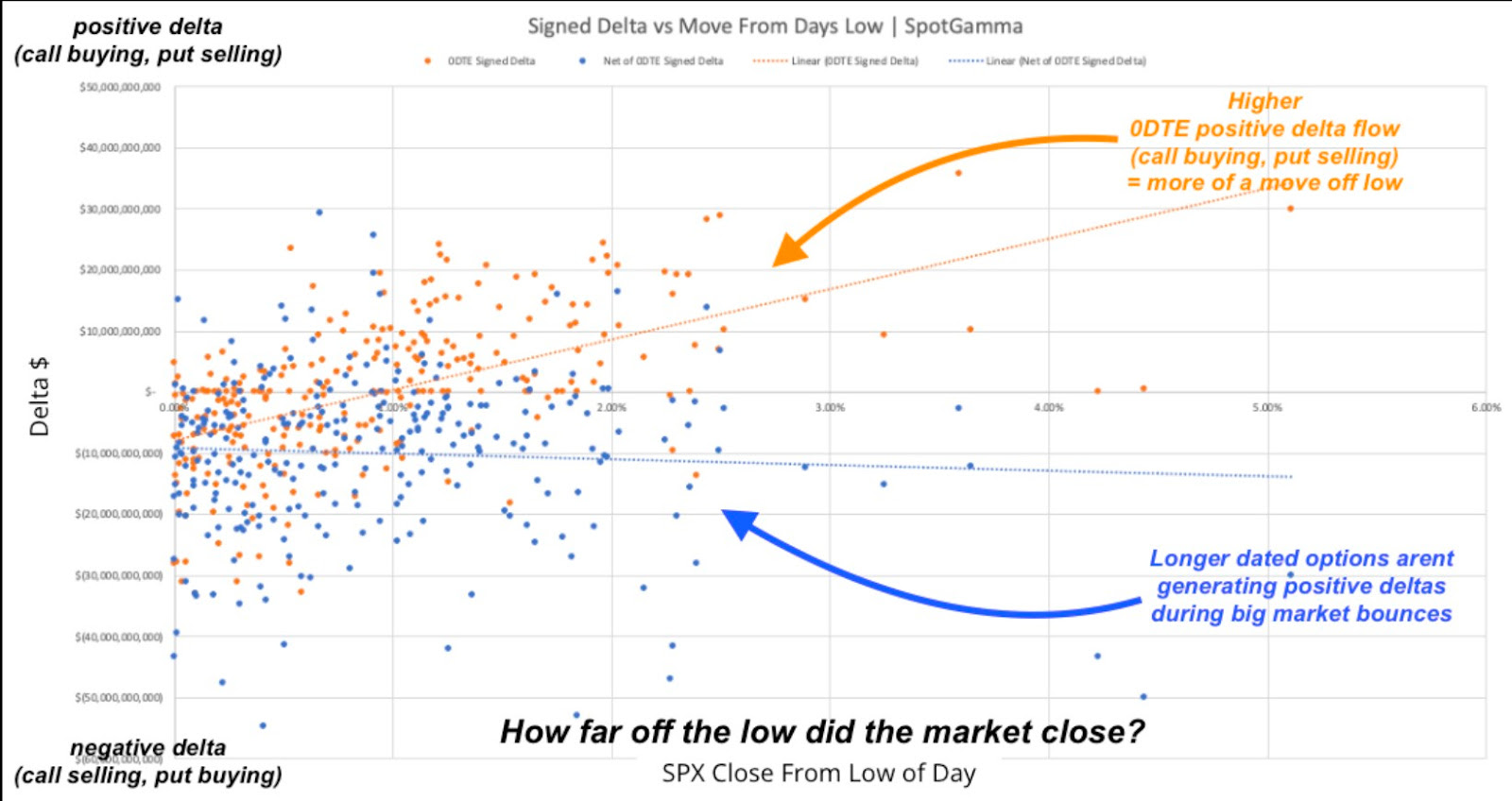
Investors are hedging against potential volatility spikes like those seen on August 5, 2024, when the VIX exploded higher. While the S&P 500 grinds upward and the VIX drifts lower and appears cheap (<16), the VVIX—“VIX of the VIX”—remains elevated. This unusual divergence manifests from demand for VIX calls, suggesting the market worries sharp repricings of risk are more likely than broad equity selloffs. The dynamic boils down to supply and demand; SPX options remain underappreciated—why protect when the market seems stable—meanwhile, VIX options are in demand, bolstering VVIX.
SpotGamma highlights this massive VIX call buying, noting dealer short convexity positioning suggests that, should volatility “wake up,” there could be significant downside pressure on equities and upside pressure on volatility, reinforcing the view that the VVIX’s elevated levels could signal a potential volatility spike, rather than a broad market crash.

“The aforementioned vega supply is indeed large, but it is innocuous unless provoked,” SpotGamma’s founder Brent Kochuba explains. Still, “with correlation stretched and IVs at lows, there is the potential for an SPX index short vol cover/single stock spasm to push into this upside vega convexity – something that we think a sharp NVDA [earnings] miss could spark.”

#2 – Options Selling and the ‘Buy My Course’ Gurus
Investors are leaning toward short-dated options selling (sometimes packaged within an ETF structure, without regard for price and thoroughly assessing broader market positioning) and structured products.

As QVR Advisors’ Benn Eifert explains, dynamic creates opportunity: deep out-of-the-money, long-dated volatility in single stocks looks attractive for tail-risk hedging. But there’s a catch—the persistence of this activity reinforces spot-vol covariance (i.e., the relationship between the underlying movements or spot and its volatility or vol). If the market shifts and volatility rises as the underlying asset moves up/down (the usual pattern flips), long volatility positions could become highly profitable, as it is then they would benefit from this reversal in spot-vol dynamics (e.g., 2020).

As SpotGamma elaborated, if strength through earnings persists, “it will supply a final equity vol and correlation drop (a ‘final vol squeeze’), ushering in a blow-off equity top. At the same time, these metrics are low enough to justify owning 3-6 month downside protection, as bad things usually happen from these vol levels.”

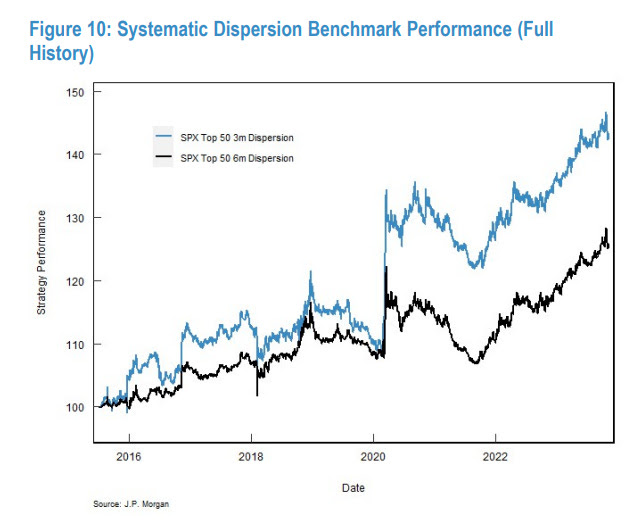
As an aside, implied correlation measures the degree to which the prices of the assets in the basket are expected to move together (positively correlated) or in opposite directions (negatively correlated). Low correlation, in this case, indicates that the stocks are expected to move independently or in opposite directions; hence, dispersion trades betting on this have performed well.

#4 – The Changing Narrative of Bitcoin and Its Maximalists
Similar patterns emerge in bitcoin. As countries face currency debasement and economic stresses, bitcoin stands out as a hedge to some. Like equities, bitcoin options are underappreciated.
For example, implied volatility has traded under 50% for one-month options, representing an attractive entry point for those looking to position themselves for a surge. This low volatility environment in Bitcoin mirrors the opportunities in equities. Here, bitcoin benefits from any volatility reversal, presenting a compelling case for those looking to participate in a big market move.

Context Applied: Trade Structuring
Trade structuring this year is all about creativity. We’ve added the following to our portfolios.
#1 – Rates
One efficient structure for safeguarding cash is the box spread, which offers several key benefits: a convenience yield, capital efficiency (especially for users of portfolio margin), easy execution via most retail brokers, and favorable tax treatment—60% long-term and 40% short-term if executed using cash-settled index options (e.g., SPX). This strategy combines a bull call spread and a bear put spread, matching lower and higher strikes and the same expiration date.
We frequently trade such structures. For instance, here’s one we purchased at the beginning of this year: BOT +1 IRON CONDOR SPX 100 (Quarterlys) 31 DEC 25 4000/7100/7100/4000 CALL/PUT @2964.25 CBOE
In this case, we invest $296,425 now to receive $310,000 in a year. This represents an implied interest rate of 5.32% or ((3100-2964.25)/2964.25)*(365/314)=0.053234. Note that there is a convenience yield, and that’s due to counterparty risk, as box spreads depend on the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC) to guarantee the transaction.
Tools like boxtrades.com help with tracking yields and finding attractive box structures.

Box trades unlock the power of yield stacking, enhancing returns by layering multiple exposures without increasing capital outlay. They preserve full buying power with portfolio margin for margin-intensive trades like synthetic longs.
For non-portfolio margin traders, yield stacking is less applicable. Instead, you can allocate ~95% of cash to box spreads, locking in your principal at maturity while risking only ~5% (the interest you stand to make), with limited downside.

#2 – Upside
Low correlation and subdued implied volatility signal stability, but any disruption could spark sharp moves.
As we explained better in Reality Is Path-Dependent, Cem Karsan notes that a slow grind higher cheapens options, fueled by continued volatility selling. Eventually, realized upside volatility will surpass implied, prompting smart money to buy options at these discounts. If the VIX holds steady or rises, it suggests fixed-strike volatility is creeping up, potentially forcing options counterparties to cut exposure or hedge, boosting markets higher; increased call demand could push counterparties to hedge by buying the underlying asset, reinforcing stability and giving a floor to options prices and the market by that token.
The play here? Replace stock exposure with options. You can buy calls outright and hedge them by selling stock—gains on the calls should outpace hedge losses. Karsan has talked about this a lot. One of our moves is to structure broken-wing butterflies or similar: buy an option near the money, sell a larger number of options further out, and cap risk with an even farther out option. In this environment, you can often put on these trades for little cost and exit at multiples higher if the market drifts sideways or up. Please see our website for case studies and example trades.
Don’t overlook crypto, either. Implied volatility remains underappreciated in bitcoin, making synthetic exposures compelling. Swapping spot for synthetic alternatives is a play on these opportunities. Though we haven’t touched them, check out Cboe’s cash-settled options on spot bitcoin: the Cboe Bitcoin US ETF Index (CBTX) and Cboe Mini Bitcoin US ETF Index (MBTX).
#3 – Hedging
Though less attractive now, VIX calls and call spreads remain a powerful tool for hedging tail risks. In our Reality Is Path-Dependent letter, we explore this topic further.
There are more compelling structures within the S&P 500 complex, particularly back spreads. For example, a put back spread involves selling a higher strike put option and buying a larger number of lower strike put options, positioning you to profit from substantial volatility shifts—similar to what we saw on August 5, 2024.
Although this structure takes advantage of the market’s unappealing volatility skew, drift presents challenges; if volatility fails to perform well during a downturn, you risk losing more money than you initially invested in the spread. Caution!

Bonus: From the White House to Wall Street
We had the opportunity to catch up with Steven Orr, founder of Quasar Markets. We discussed his career and the future of fintech and trading technology. Before Quasar Markets, Orr worked as an executive at Money.net and Benzinga. He also serves on the board of the American Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Association. His diverse background includes positions with the White House, the U.S. State Department, the PGA Tour, the NBA, and various professional sports leagues. Orr frequently shares his insights on TV and appears at events like the World Economic Forum. Check it out, and thank you, Steven!
Disclaimer
By viewing our content, you agree to be bound by the terms and conditions outlined in this disclaimer. Consume our content only if you agree to the terms and conditions below.
Physik Invest is not registered with the US Securities and Exchange Commission or any other securities regulatory authority. Our content is for informational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice or a recommendation to buy or sell any security or other investment. The information provided is not tailored to your financial situation or investment objectives.
We do not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, or timeliness of any information. Please do not rely solely on our content to make investment decisions or undertake any investment strategy. Trading is risky, and investors can lose all or more than their initial investment. Hypothetical performance results have limitations and may not reflect actual trading results. Other factors related to the markets and specific trading programs can adversely affect actual trading results. We recommend seeking independent financial advice from a licensed professional before making investment decisions.
We don’t make any claims, representations, or warranties about the accuracy, completeness, timeliness, or reliability of any information we provide. We are not liable for any loss or damage caused by reliance on any information we provide. We are not liable for direct, indirect, incidental, consequential, or damages from the information provided. We do not have a professional relationship with you and are not your financial advisor. We do not provide personalized investment advice.
Our content is provided without warranties, is the property of our company, and is protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws. You may not be able to reproduce, distribute, or use any content provided through our services without our prior written consent. Please email renato@physikinvest for consent.
We reserve the right to modify these terms and conditions at any time. Following any such modification, your continued consumption of our content means you accept the modified terms. This disclaimer is governed by the laws of the jurisdiction in which our company is located.